Introduction
Supply chain management (SCM) is becoming increasingly complex, businesses need innovative ways to manage and optimize their operations. supply chain analytics has emerged as a transformative solution that enables organizations to gain actionable insights, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Key Takeaways
Supply chain analytics involves applying data collection, processing, and analysis techniques to improve decision-making across the supply chain.
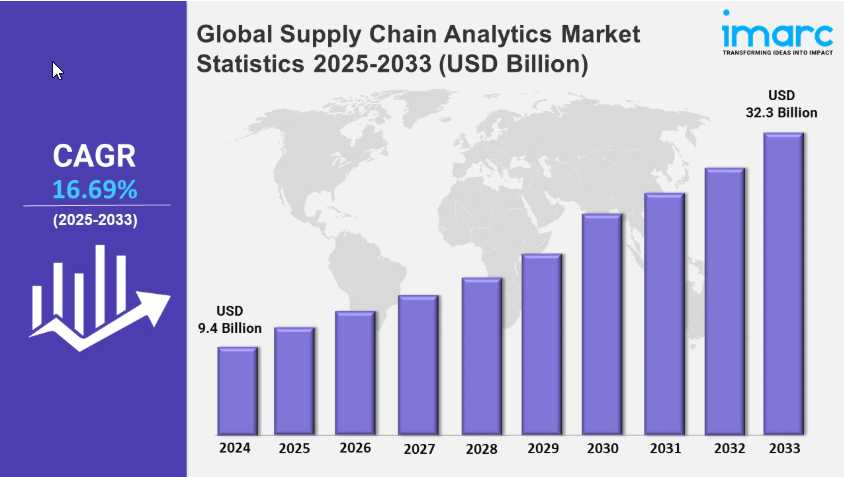
The global supply chain analytics market is expected to reach USD 32.3 Billion by 2033, indicating significant industry growth and adoption.
Types of Analytics:
- Descriptive analytics
- Predictive analytics
- Prescriptive analytics
- Cognitive analytics
Supply chain analytics enhances visibility, enables informed decision-making, improves risk management, reduces costs, and boosts customer satisfaction.
Analytics helps in demand forecasting, inventory optimization, supplier performance evaluation, logistics optimization, and real-time tracking.
Supply chain analytics follows a systematic process of data collection, integration, processing, analysis, and action implementation.
Define Supply Chain Analytics
Supply chain analytics refers to the application of data collection, processing, and analysis techniques to improve the decision-making processes across the supply chain. It combines advanced technologies, such as big data analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning, to provide actionable insights that streamline supply chain operations.
It helps businesses identify inefficiencies, predict trends, and make informed decisions to stay competitive by analyzing data from procurement, production, inventory management, and logistics.
History of Supply Chain Analytics
The roots of supply chain analytics can be traced back to the late 20th century when companies began using statistical models and computer-based tools to optimize logistics. Initially, these efforts focused on improving inventory management and transportation networks.
In the 1990s, enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems advancements enabled organizations to integrate supply chain processes and gather large amounts of data. The 2000s saw the rise of big data and predictive analytics, which revolutionized supply chain management by allowing businesses to anticipate market trends and consumer behavior.
Today, supply chain analytics has evolved into a sophisticated field that incorporates cognitive computing, artificial intelligence, and real-time data processing, making it an indispensable tool for modern enterprises.
Different Types of Supply Chain Analytics
It can be categorized into four primary types, each serving a unique purpose in the decision-making process.
- Descriptive analytics
- Predictive analytics
- Prescriptive analytics
- Cognitive analytics
1. Descriptive analytics
Descriptive analytics analyzes historical data to understand past performance and identify trends or patterns. For instance, businesses can use this type of analytics to determine seasonal demand fluctuations or evaluate supplier performance.
Example Use Case: Retailers analyzing last year’s holiday sales data to plan inventory levels.
2. Predictive analytics
Predictive analytics uses statistical models and machine learning algorithms to forecast future outcomes. It helps businesses anticipate demand, manage risks, and prepare for potential disruptions.
Example Use Case: Predicting the impact of geopolitical events on raw material availability.
3. Prescriptive analytics
Prescriptive analytics goes beyond predictions by recommending the best course of action to achieve desired outcomes. This type of analytics uses advanced optimization algorithms to provide actionable solutions.
Example Use Case: Optimizing delivery routes to reduce shipping costs.
4. Cognitive analytics
Cognitive analytics leverages artificial intelligence and machine learning to simulate human-like reasoning and decision-making. It processes unstructured data, such as social media posts or news articles, to provide deeper insights.
Example Use Case: Analyzing customer sentiment to predict changes in product demand.
Why is Supply Chain Analytics Important?
It helps businesses to stay agile and competitive. Here’s why it is indispensable:
- Enhanced Visibility: It provides a holistic view of the supply chain, from procurement to final delivery.
- Informed Decision-Making: Analytics-driven insights enable data-backed decisions, reducing guesswork.
- Risk Management: Predictive models help identify and mitigate potential risks, such as supplier failures or market volatility.
- Cost Reduction: Optimizing routes, inventory levels, and procurement processes leads to significant cost savings.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: By aligning supply chain processes with customer expectations, businesses can ensure timely deliveries and high-quality products.
How Supply Chain Analytics Help Improve Efficiency
1. Demand Forecasting
Accurate demand predictions prevent overstocking and understocking, ensuring the right products are available at the right time.
2. Inventory Optimization
Analytics helps maintain optimal inventory levels, reducing carrying costs and minimizing waste.
3. Supplier Performance Evaluation
By analyzing supplier data, businesses can identify reliable partners and negotiate better contracts.
4. Logistics Optimization
Advanced analytics tools help streamline transportation routes, reduce fuel consumption, and improve delivery times.
5. Real-Time Tracking
With real-time data, businesses can monitor shipments and proactively address delays or disruptions.
How Supply Chain Analytics Works
It follows a systematic process to transform raw data into actionable insights:
- Data Collection: Gathering data from various sources, including ERP systems, IoT devices, and external databases.
- Data Integration: Consolidating data into a unified platform for analysis.
- Data Processing: Cleaning and organizing data to ensure accuracy.
- Analysis: Applying statistical models, machine learning algorithms, and visualization tools to derive insights.
- Action: Implementing strategies based on the insights gained.
Supply Chain Analytics and Master Data Management
Master Data Management (MDM) ensures that critical business data is consistent, accurate, and up to date across the organization. Integrating MDM with analytics enhances decision-making by providing a reliable data foundation.
For example, clean and consistent supplier data enables accurate risk assessments and better contract negotiations. Similarly, unified product data ensures smooth inventory management and demand planning.
Key Features of Effective Supply Chain Analytics
- Real-Time Data Processing: Enables instant responses to supply chain disruptions.
- Scalability: Supports growing data volumes and expanding business operations.
- User-Friendly Dashboards: Provides intuitive visualizations for quick decision-making.
- Advanced Predictive Models: Helps anticipate future trends and challenges.
- Integration Capabilities: Seamlessly connects with ERP, WMS, and other enterprise systems.
Conclusion
Supply chain analytics is no longer a luxury but a necessity in today’s fast-paced business environment. It empowers organizations to optimize operations, reduce costs, and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
As businesses continue to face evolving challenges, embracing supply chain analytics will be crucial for staying competitive and resilient. By leveraging advanced tools and techniques, companies can transform their supply chains into strategic assets that drive growth and innovation.
Commport Business Analytics Solution
Top 30 KPIs you should track to improve your supply chain efficiency.
Commport business analytics solutions can help you track these metrics continuously with real-time data insights and dashboards.
Download NowFrequently Asked Questions
Commport Communications offers tailored business analytics solution that integrate advanced analytics, MDM, and real-time data processing to optimize supply chain operations.
AI powers predictive and cognitive analytics, enabling businesses to anticipate trends and automate decisions.
Industries such as retail, manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics benefit significantly from SCA.
Integrating MDM with analytics ensures consistent and accurate data for better decision-making.
Real-time data enables businesses to respond quickly to disruptions and ensure seamless operations.