Introduction
How Does EDI Work?
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) works by automating the electronic exchange of business documents between organizations in a standardized format. EDI replaces traditional paper-based communication, reducing errors and improving transaction speed. Common EDI documents include purchase orders, invoices, shipping notices, and payment confirmations.
There are three main components to sending EDI documents:
- Prepare
- Translate
- Transmit
EDI Workflow Diagram
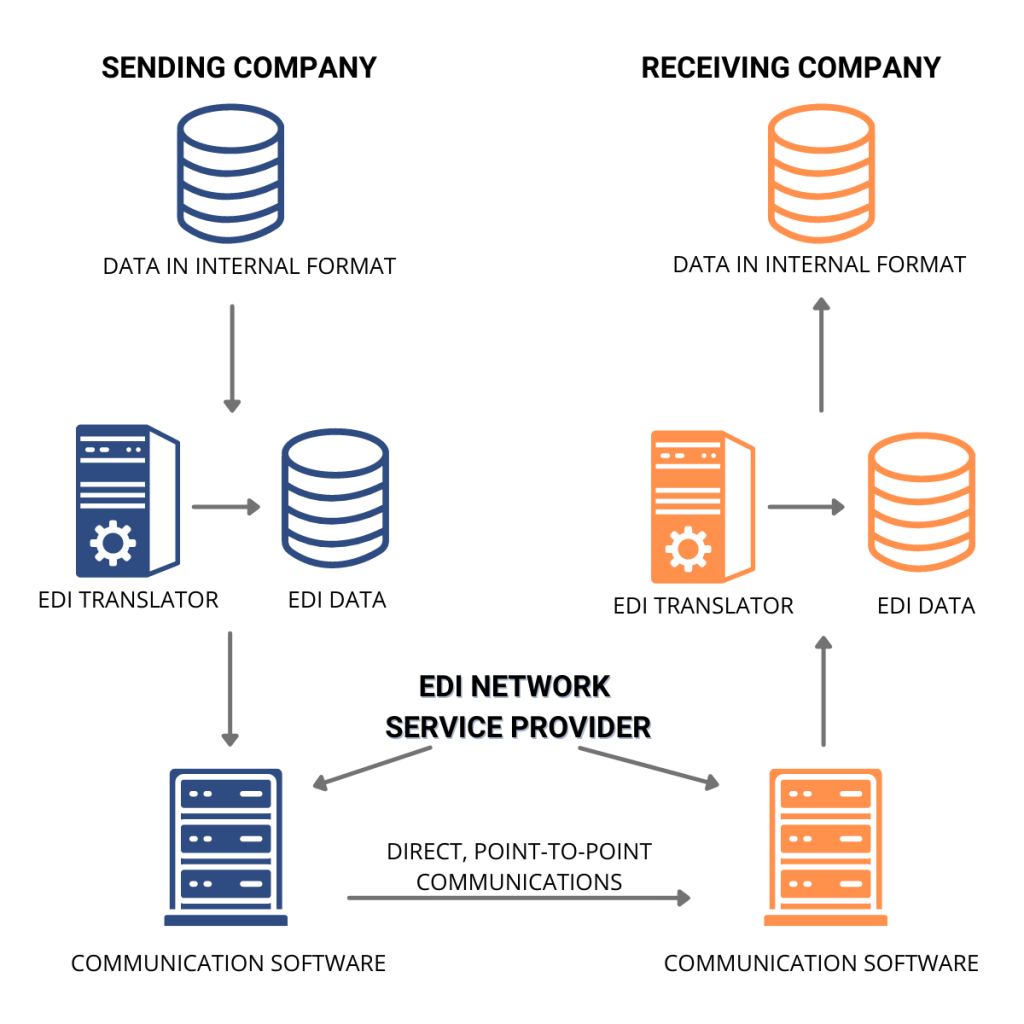
Step 1: Prepare the documents to be sent
EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) requires electronic versions of files. Instead of printing a paper purchase order, you would organize the necessary information to build an EDI document within your system. The sources of the data and the methods available to generate the electronic documents can include:
- Data entry by human intervention
- Exporting data from Excel spreadsheets or internal databases
- Reformatted electronic reports into data files
Step 2: Translate documents into EDI format
Put your collected internal electronic data through EDI translation software to convert it into the EDI standard format. EDI standards describe the format in which the data will be sent and received. Most common standard sets:
- American National Standards Institute (ANSI X12) in North America
- UN/EDIFACT globally
There are two ways to use translation software;
You can purchase EDI translation software that you have to manage and maintain on your premises. This requires dedicated IT resources with specialized mapping expertise to define how your internal data is to be mapped to the EDI data.
Alternatively, an EDI service provider would provide translation services. Using this option you would send your electronic data to the EDI Service provider, who would then handle all mapping, translation, and support to and from the EDI format on your behalf.
Step 3: B2B Connection and Transmission of your EDI documents
Once your business documents are translated to the appropriate EDI format they are ready to be sent to your business partners. There are several types of EDI for this connection:
- Secure internet protocol (AS2)
- Connect to an EDI Network provider with a Value Added Network (VAN)
- A combination of both, depending on the particular partner and the volume of transactions you expect to exchange.
Key Components of EDI
To facilitate seamless data exchange, EDI relies on several key components:
EDI Standards – Define the format and structure of EDI messages (e.g., ANSI X12, UN/EDIFACT, TRADACOMS).
EDI Software – Translates business documents into EDI formats and vice versa.
EDI Network – The medium through which EDI transactions are transmitted, including Direct EDI, VANs, and API-based solutions.
EDI Mapping – Defines how data elements in a company’s internal system correspond to EDI standard formats.
Types of Common EDI X12 Transactions
EDI 850 – Purchase Order
EDI 810 – Invoice
EDI 856 – Advance Ship Notice (ASN)
EDI 940 – Warehouse Shipping Order
EDI 997 – Functional Acknowledgment
- EDI 876 – Grocery Products Purchase Order Change
How EDI Helps with Supply Chain Management
EDI helps optimize supply chain management by enabling real-time data exchange between suppliers, manufacturers, logistics providers, and retailers. Here’s how EDI improves supply chain operations:
Faster Order Processing – Automates purchase order and invoice exchange, reducing order fulfillment times.
Improved Inventory Management – Enables real-time tracking of inventory levels, minimizing stockouts and overstock situations.
Enhanced Supplier Collaboration – Facilitates seamless communication with suppliers, improving demand forecasting and replenishment planning.
Optimized Logistics & Shipping – Automates shipping notices and transportation documents, ensuring on-time deliveries.
Reduced Supply Chain Costs – Eliminates manual paperwork, reducing administrative costs and transaction errors.
Greater Visibility & Traceability – Provides end-to-end visibility into the supply chain, enabling proactive decision-making.
Conclusion
EDI operates on the principles of standardized electronic communication, facilitating the seamless exchange of business documents between trading partners. By eliminating manual processes, reducing errors, and enhancing the speed of transactions, EDI serves as a foundational tool in modernizing and optimizing business operations. The interoperability and efficiency it brings contribute significantly to building robust and agile supply chains in today’s dynamic and interconnected business environment.
Download: EDI Buyers Guide
Unlock the full potential of your supply chain with our comprehensive EDI Buyer's Guide — your first step towards seamless, efficient, and error-free transactions
Frequently Asked Questions
EDI uses standardized formats to encode and structure business documents. These documents are then electronically transmitted between trading partners, ensuring a consistent and machine-readable exchange of information.
The key components include the EDI software or service provider, communication protocols (such as AS2 or FTP), standardized document formats (like EDIFACT or X12), and secure networks. These elements work together to enable the efficient flow of data.
EDI reduces errors by eliminating manual data entry. The standardized formats and automated processes significantly minimize the risk of errors that often accompany traditional paper-based methods.
Yes, EDI is designed to integrate seamlessly with various business systems, including Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Warehouse Management Systems (WMS). This integration ensures a cohesive flow of data across different facets of the business.
EDI is suitable for businesses of all sizes. Many EDI solutions offer scalability, making them adaptable to the specific needs and volumes of small enterprises. The benefits of efficiency, accuracy, and improved collaboration are accessible to businesses regardless of their scale.