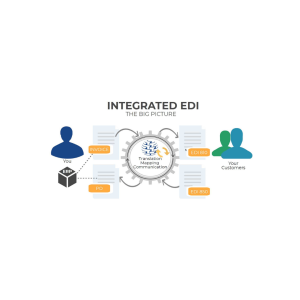
Intoduction
Most organizations embark on an EDI journey in response to an identified business problem or opportunity. Many times a large customer will ask to exchange their supply chain transactions using EDI and that is oftentimes the starting point. Other times, organizations find themselves in a position where they don’t have the information they need, when they need it, which leads them to use EDI to help solve that problem.
So, you have found yourself embarking on an EDI journey… but you aren’t sure what path you should take.
17 Questions to Ask Yourself Before Getting Started with EDI
- Are you familiar with EDI? if not read this complete EDI guide
- Do you have an existing EDI solution?
- What do you like about it?
- What don’t you like about it?
- What would you like to see changed?
- Are you responding to a customer mandate?
- How much business do you have with that customer?
- Do you have other customers who have requested an EDI connection with you that you haven’t actioned?
- How much business do you have with that (those) customer(s)?
- What resources do you have available to spend on EDI?
- In terms of the initial selection of a solution or provider as well as on a day-to-day basis?
- What systems and business processes are you already using?
- How will engaging with an EDI process affect your operations?
- Should you consider integration?
- Are you getting the information you need to operate your business, in a timely fashion?
- What kind of timeline are you working towards?
- How much does an EDI solution cost?
Next Steps: How to Choose & Implement Effective EDI Solution?
1. Understand the Basics of EDI
Before diving into implementation, it’s important to grasp the fundamental concepts of EDI VAN. Essentially, EDI involves the electronic exchange of structured business documents, such as purchase orders, invoices, and shipping notices, in a standardized format that can be easily understood by computers. Familiarize yourself with EDI terminology, standards (e.g., ANSI X12, EDIFACT), and common document types.
2. Assess Your Business Needs
Identify the specific pain points in your current business processes that EDI can address. Determine the volume of transactions, the complexity of trading partner relationships, and the desired outcomes. Analyze the potential benefits of implementing EDI, including improved accuracy, faster order processing, reduced costs, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
3. Select an EDI Solution
There are various options for implementing EDI, ranging from in-house systems to cloud-based EDI service providers. Consider factors such as budget, IT infrastructure, scalability, and resource availability. In-house solutions offer more control but require significant investments in hardware, software, and ongoing maintenance. Alternatively, partnering with a reliable EDI provider can offer a cost-effective and hassle-free implementation.
4. Establish Trading Partner Relationships
To engage in EDI, you need to establish relationships with your trading partners. Identify the key stakeholders and determine their EDI capabilities. Understand their preferred communication protocols, document formats, and technical requirements. Collaborate with your partners to align processes, define data mappings, and establish testing procedures.
5. Plan for System Integration
Evaluate your existing business systems, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) or Order Management Systems (OMS), to determine their compatibility with EDI. Consult with your IT team or solution provider to ensure seamless integration between your internal systems and the EDI platform. Evaluate the need for additional middleware or adapters to facilitate data transformation and transmission.
6. Implement and Test
Begin the implementation process by configuring your chosen EDI solution to accommodate your business requirements and trading partner specifications. Create maps to convert data from internal systems to EDI formats and vice versa. Conduct thorough testing with your trading partners to validate the EDI transactions, ensuring data accuracy and adherence to standards. Address any issues or discrepancies promptly.
7. Monitor and Maintain
Once your EDI system is operational, establish monitoring mechanisms to ensure smooth functioning. Regularly review error logs, transaction status, and performance metrics to detect and resolve any issues promptly. Stay up-to-date with evolving EDI standards and trading partner requirements. Periodically assess the effectiveness of your EDI implementation, identify areas for improvement, and implement necessary adjustments.
8. Expand and Optimize
EDI implementation is a continuous journey. As you gain experience and confidence, consider expanding your EDI capabilities by onboarding new trading partners or adding additional transaction types. Explore opportunities for further process optimization, such as integrating advanced functionalities like automated acknowledgments, advanced shipping notifications (ASNs), or barcoding systems.
Conclusion
Implementing EDI is a strategic decision that can significantly enhance your business operations, efficiency, and competitiveness. By understanding the basics, selecting the right EDI solution provider, establishing strong trading partner relationships, and ensuring seamless integration, you can successfully embark on your EDI journey. Remember to monitor and optimize your EDI processes as you scale your business.
Download: EDI Buyers Guide
Unlock the full potential of your supply chain with our comprehensive EDI Buyer's Guide — your first step towards seamless, efficient, and error-free transactions
The initial steps include understanding your business processes, identifying the EDI transactions you need, selecting a suitable EDI solution or provider, and establishing communication with trading partners to ensure a coordinated implementation.
Yes, you will need EDI software or a service provider, as well as a reliable internet connection. The hardware requirements are generally minimal and depend on whether you choose on-premise or cloud-based EDI solutions.
Assess your business processes and communication needs. Identify the transactions commonly used in your industry and those required by your trading partners. This analysis will guide you in determining the specific EDI transactions you need to implement.
While EDI implementation can vary in complexity based on business size and requirements, many modern EDI solutions are designed for ease of use. The implementation timeline depends on factors such as the scope of integration and the readiness of your business processes, with some implementations taking weeks and others a few months.
Training is crucial to ensure that your team is proficient in using the chosen EDI solution and understands the new processes. Most EDI providers offer training programs, and investing in these sessions ensures that your team can confidently navigate the EDI system, reducing the learning curve and potential errors during the transition.