Introduction
Did you know that hundreds of patients face problems from medical errors annually worldwide? This sobering statistic from the Institute of Medicine’s report highlights why building a high-reliability organization in healthcare isn’t just important—it’s critical.
However, there’s hope. Healthcare facilities that have implemented HRO principles have seen remarkable results. Some organizations have reported up to 83% fewer serious safety events within just two years. That’s why leading healthcare institutions are increasingly adopting high-reliability practices, focusing on creating environments where errors are prevented before they occur.
However, research shows how successful healthcare HROs operate and found that the key lies in five core principles:
- Sensitivity to operations
- Reluctance to simplify
- Preoccupation with failure
- Deference to expertise
- Commitment to resilience
Also, we are going to discuss how B2B integration solutions can help HROs in healthcare streamline their data processing, improve supply chain efficiency, and achieve compliance.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll show you exactly how to transform your healthcare organization into a high-reliability powerhouse step by step.
What is a High Reliability Organization in Healthcare?
A high-reliability organization (HRO) in healthcare consistently delivers safe, efficient, and high-quality care, even when facing complex challenges and high-risk situations. These organizations operate with exceptional consistency in achieving their goals while avoiding potentially catastrophic errors.
Key characteristics of HROs
High-reliability organizations in healthcare demonstrate five fundamental principles that set them apart. First, they maintain constant sensitivity to operations, where leaders and staff remain acutely aware of systems and processes affecting patient care. Additionally, these organizations show a reluctance to simplify, recognizing that while streamlining processes is beneficial, oversimplification can mask underlying problems.
Furthermore, successful HROs cultivate a preoccupation with failure, encouraging every employee to identify potential breakdowns in work processes. They also practice deference to expertise, valuing insights from staff with the most pertinent safety knowledge, regardless of their position in the hierarchy. Lastly, these organizations prioritize resilience, preparing teams to respond swiftly to unexpected events.
Why healthcare needs high reliability
Healthcare organizations face unique challenges, including higher workforce mobility and the complexity of caring for patients rather than machines.
Modern healthcare facilities operate in an environment of rapid innovation, specialized departments, and emerging diseases. This complexity, coupled with the potential for life-threatening errors, makes the adoption of HRO principles particularly crucial. Furthermore, the healthcare sector deals with an unprecedented amount of health information, which the World Health Organization has termed an “infodemic”.
Essential HRO Principles for Healthcare
The five essential principles of high-reliability organizations form the foundation for achieving exceptional patient safety and quality care. Let us explore each principle and understand its significance in healthcare settings.
1. Preoccupation with failure
A mindset focused on detecting potential failures distinguishes successful healthcare HROs. This approach involves continuous attention to anomalies that might signal larger system problems. Instead of viewing near-misses as proof of effective safeguards, organizations treat them as opportunities for system improvement.
Daily safety huddles serve as a crucial platform where frontline staff discuss incidents, observations, and concerns. Through these discussions, teams strengthen their culture of preoccupation with failure across the organization. Subsequently, reporting good catches becomes equally important as reporting adverse events.
2. Reluctance to simplify
Although streamlining processes benefits healthcare operations, oversimplification can mask critical issues. High-reliability organizations understand that their systems might fail in unprecedented ways. Therefore, they encourage diverse perspectives and opinions to guard against oversimplification.
For instance, during patient safety analyses, instead of simply attributing errors to individual performance, organizations examine the underlying care processes and systems. This comprehensive approach helps identify multiple factors contributing to adverse outcomes.
3. Sensitivity to operations
Maintaining constant awareness of care delivery processes enables quick identification of potential errors. Frontline teams often notice and respond first to small operational changes. Thus, establishing clear, accessible, and non-punitive communication channels between frontline staff and leadership becomes essential.
Leaders must stay fully informed about care delivery processes to recognize threats, identify risks, and prevent errors. This principle encourages proactive communication and problem-solving rather than reactive responses.
4. Commitment to resilience
Despite best efforts and past safety successes, healthcare errors occur. Organizations with highly reliable cultures quickly contain errors, enabling continued function despite setbacks. Teams receive training in performing rapid situational assessments and preparing for system failures.
Resilient organizations focus on:
- Crisis management training for handling high-pressure situations
- Anticipating potential failures through resilience engineering
- Supporting staff mental health resources for stress management
- Emphasizing continuous learning from incidents
5. Deference to expertise
In high-reliability healthcare organizations, expertise takes precedence over authority. During rapidly changing, high-risk conditions, on-ground subject matter experts become essential for urgent situational assessment and response.
For example, physicians must overcome the need for autonomy and infallibility, encouraging system responsibility for patient care. This approach enables teams to leverage insights from staff with the most pertinent safety knowledge, regardless of their position in the hierarchy.
Building Your HRO Implementation Plan
Successful implementation of HRO principles requires a structured approach and careful planning. Based on data from healthcare organizations that have achieved high reliability status, specific strategies emerge as crucial elements for success.
Assess current state
First, conduct a comprehensive performance readiness assessment using validated tools like the Joint Commission’s Oro 2.0 High Reliability Assessment. This evaluation helps identify gaps in safety performance, leadership commitment, and staff engagement levels.
Organizations should focus on three key areas during assessment:
- Current safety culture and communication protocols
- Data systems and tracking capabilities
- Staff training needs and resource allocation
Establishing work groups dedicated to specific aspects of HRO implementation strengthens the assessment process. These teams analyze existing practices, identify potential barriers, and develop targeted solutions for improvement.
Set clear goals
Following assessment, organizations must establish clear, measurable objectives. Successful healthcare HROs prioritize these fundamental goals:
- Leadership Development: Create a governance structure that manages quality improvement across all organizational levels. Leadership must demonstrate unwavering commitment to achieving zero harm through consistent messaging and visible support.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Implement robust systems to:
- Track and display quality measures
- Aggregate performance data
- Train staff in data interpretation
- Identify actionable insights for improvement
- Staff Engagement: Design comprehensive training programs that:
- Educate all personnel on process improvement techniques
- Foster continuous learning opportunities
- Create quality champion change agents
- Promote systematic problem-solving approaches
Notably, organizations should anticipate potential implementation challenges. Common barriers include competing priorities, such as electronic medical record system implementations and associated costs. To overcome these obstacles, many successful HROs partner with external consultants who specialize in healthcare performance improvement.
Regular crisis management drills serve as essential tools for testing and refining implementation progress. These simulations help teams identify gaps in communication, response protocols, and resource allocation before real emergencies occur.
Furthermore, establishing clear communication channels proves vital for implementation success. Organizations must create systems that encourage transparency and information sharing across all levels. This approach enables quick identification and resolution of potential safety issues while fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
To maintain momentum, successful HROs implement regular feedback mechanisms that measure progress toward established goals. These mechanisms help organizations remain agile and responsive to changing healthcare demands while maintaining their focus on high reliability principles.
Creating a Culture of Safety
Building a culture of safety stands as the cornerstone of successful high reliability organizations in healthcare.
Leadership commitment strategies
Effective leaders in healthcare HROs prioritize physical and psychological safety as prerequisites for patient safety.
Leaders must fulfill four essential responsibilities:
- Guard the learning system through nonpunitive transparency
- Create psychological safety for voicing concerns
- Foster trust through nonnegotiable respect
- Ensure value alignment in all decisions
Staff engagement techniques
Successful staff engagement begins with establishing workplace safety protocols and solid reporting procedures for potential risks. Organizations achieve this through:
Interdepartmental Collaboration: Creating teams comprising nurses, laboratory technicians, physicists, and physicians fosters strong social connections and builds a sense of belonging. This approach enables staff to share ideas openly without fear of retribution.
Recognition Programs: Houston Methodist celebrates safety achievements through ‘good catch’ awards at Board meetings and annual Culture of Safety awards for individuals and teams. These programs reinforce positive behaviors and encourage continued vigilance.
Communication protocols
Clear communication serves as the foundation for maintaining situational awareness and preventing errors.
Clinical teams receive training in using specific, nonconfrontational language for raising concerns:
- “Doctor, I need clarification of this order”
- “I am Concerned”
- “I am Uncomfortable”
- “This is a Safety issue”
Operational transparency ensures activities involved in the learning process remain visible to leaders, staff, patients, families, and the community. Through leadership safety briefs and huddles, organizations share critical information across all levels within two hours of occurrence.
In situations involving potential harm, organizations employ Just Culture principles, focusing primarily on identifying system issues rather than individual blame. This approach encourages open reporting and continuous improvement while maintaining individual accountability for conscious disregard of clear risks.
Through these coordinated efforts, healthcare organizations create environments where staff feel empowered to speak up about safety concerns. Consequently, teams develop shared understanding, anticipate potential problems, and manage situations effectively – even those involving conflict.
Measuring HRO Success
Tracking progress toward high reliability requires robust measurement systems and well-defined metrics. Organizations must implement comprehensive evaluation tools to assess their journey effectively.
Key performance indicators
Successful healthcare HROs monitor several critical metrics to evaluate their progress.
You can make significant improvements through focused measurement:
- Increased patient safety event reporting rates
- Enhanced patient safety culture scores
- Reduced standardized mortality rates
- Decreased complication rates
The Joint Commission’s High Reliability Health Care Maturity (HRHCM) model emerged as the most rigorously developed tool for measuring HRO progress. This comprehensive framework evaluates organizations across multiple dimensions:
- Leadership commitment
- Safety culture development
- Process improvement implementation
- Staff training effectiveness
- Patient safety intervention outcomes
Data collection methods
Healthcare facilities employ various tools and approaches to gather meaningful data. The Oro™ 2.0 High Reliability Assessment Tool stands out as the most validated measurement instrument, having been tested across 52 US hospitals. This online assessment helps executive teams:
- Identify current high-reliability maturity levels
- Understand organizational strengths and gaps
- Chart progress toward zero harm goals
- Track implementation effectiveness
Organizations typically utilize a combination of measurement approaches six crucial leadership domains:
- Vision establishment
- Trust and inclusion building
- Board selection and development
- Leadership prioritization
- Just culture promotion
- Behavioral expectation setting
Continuous measurement strategies often incorporate:
- Annual or biennial comprehensive surveys
- Regular mini-culture assessments
- Tracking of mortality and complication rates
- Monitoring patient safety event reports
- Analysis of serious safety event rates (SSER)
Significantly, healthcare HROs recognize that increased reporting of safety events initially indicates improvement rather than decline. This counterintuitive metric reflects enhanced communication and heightened safety awareness among staff members.
The Cultural Assessment Survey (CAS) offers another validated tool, demonstrating high internal reliability and strong content validity. This instrument specifically measures:
- Initial safety culture levels
- Progress in developing patient safety awareness
- Staff engagement in safety protocols
- Communication effectiveness
Ultimately, successful measurement requires organizations to maintain comprehensive data systems that can aggregate, analyze, and transform information into actionable insights. These systems enable healthcare facilities to:
- Compare performance against industry benchmarks
- Identify improvement opportunities
- Guide organizational decision-making
- Support continuous quality enhancement
How B2B Integration Solutions Help HROs in Healthcare
High Reliability Organizations (HROs) in healthcare operate in high-risk, high-complexity environments where efficiency, accuracy, and compliance are critical. These organizations—such as hospitals, healthcare systems, and large provider networks—focus on error reduction, process standardization, and operational excellence to ensure patient safety and service continuity.
B2B integration solutions like Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), Value-Added Networks (VAN), Global Data Synchronization Network (GDSN), and Business Analytics play a vital role in enhancing efficiency, data accuracy, and seamless collaboration among healthcare stakeholders. Here’s how these b2b technologies can benefit HROs in healthcare.
1. Electronic Data Interchange (EDI): Streamlining Transactions
EDI automates the exchange of standardized electronic documents between healthcare providers, suppliers, insurance companies, and regulatory bodies.
Key Benefits for HROs:
✅ Faster and More Accurate Transactions: Automates claims processing, patient record transfers, and procurement.
✅ Regulatory Compliance: Ensures adherence to industry standards for secure data exchange.
✅ Error Reduction: This minimizes manual data entry errors in billing, insurance claims, and supplier orders.
✅ Cost Efficiency: Eliminates paper-based transactions, reducing administrative overhead.
2. Value-Added Networks (VAN): Ensuring Secure and Reliable Data Exchange
Value added networks VANs act as secure intermediaries that facilitate data exchange between different healthcare entities, ensuring safe and structured communication.
Key Benefits for HROs:
🔹 Enhanced Security: Protects sensitive patient and organizational data through encrypted communication and controlled access.
🔹 Guaranteed Delivery: Ensures accurate and complete transmission of critical documents, with tracking and acknowledgment features.
🔹 Simplified Partner Connectivity: Enables integration with multiple stakeholders, even if they use different technologies.
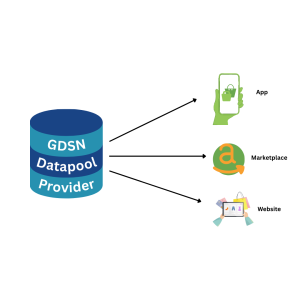
3. Global Data Synchronization Network (GDSN): Enhancing Data Accuracy in Supply Chain Management
GDSN enables real-time, standardized data sharing across healthcare organizations, particularly for medical devices, pharmaceuticals, and other supplies.
Key Benefits for HROs:
🔸 Improved Product Data Accuracy: Ensures consistency in product descriptions, expiration dates, lot numbers, and UDI (Unique Device Identification) requirements.
🔸 Efficient Supply Chain Management Reduces stockouts, inventory discrepancies, and supply chain disruptions.
🔸 Regulatory Compliance: Supports compliance with GS1 and UDI standards to meet healthcare regulations.
4. Business Analytics: Driving Data-Driven Decision Making
HROs generate vast amounts of patient, operational, and financial data that can be leveraged for better decision-making through advanced analytics.
Key Benefits for HROs:
📊 Predictive Analytics for Risk Management: Identifies potential errors or operational risks before they impact patient safety.
📊 Optimized Resource Allocation: Analyzes staffing needs, equipment usage, and supply chain efficiency to reduce waste and improve efficiency.
📊 Enhanced Financial Performance: Detects billing inefficiencies and revenue cycle improvements to optimize profitability.
📊 Performance Monitoring & Compliance: Tracks KPI benchmarks for regulatory compliance and continuous process improvements.
Conclusion
Healthcare organizations that embrace the five core principles – sensitivity to operations, reluctance to simplify, preoccupation with failure, deference to expertise, and commitment to resilience – consistently achieve better patient outcomes. These principles, combined with strong leadership commitment and staff engagement, create environments where errors decrease and safety thrives.
Data-driven measurement remains crucial for tracking progress and identifying areas for improvement. Organizations must establish robust systems to collect, analyze, and act upon safety metrics while maintaining a just culture that encourages open reporting and continuous learning.
Healthcare leaders ready to transform their organizations can benefit from expert guidance and proven solutions. Explore CommCARE Health Solutions by Commport Communications to access specialized tools and support for your HRO journey.
Remember, achieving high reliability status requires patience, dedication, and systematic effort. Start with a thorough assessment, set clear goals, engage your staff, and maintain consistent measurement practices. Though challenging, the rewards of reduced errors, enhanced patient safety, and improved outcomes make the journey worthwhile.
CommCARE Health Solutions by Commport
Frequently Asked Questions
The five key principles are: preoccupation with failure, reluctance to simplify, sensitivity to operations, commitment to resilience, and deference to expertise. These principles help healthcare organizations consistently deliver safe, efficient, and high-quality care even in complex and high-risk situations.
Healthcare organizations can measure HRO progress using tools like the Joint Commission’s High Reliability Health Care Maturity model and the Oro™ 2.0 High Reliability Assessment Tool. They should track metrics such as safety event reporting rates, patient safety culture scores, mortality rates, and complication rates.
Leadership plays a crucial role in creating an HRO by demonstrating unwavering commitment to achieving zero harm, prioritizing physical and psychological safety, fostering trust, and ensuring value alignment in all decisions. Leaders must also create an environment where staff feel empowered to voice concerns without fear of retribution.
Healthcare facilities can engage staff through interdepartmental collaboration, recognition programs for safety achievements, comprehensive training on process improvement techniques, and creating quality champion change agents. Establishing clear communication channels and encouraging transparency are also essential for staff engagement.
Common challenges include competing priorities (such as implementing new electronic medical record systems), associated costs, and initial increases in reported safety events. Overcoming these challenges often requires partnering with external consultants, maintaining strong leadership commitment, and understanding that increased reporting initially indicates improvement rather than decline in safety culture.