Introduction
Batman and Robin. LeBron and D-Wade. Peanut butter and jelly. Some partnerships are so powerful they transform the game. These dynamic duos prove that the right combination can achieve extraordinary results.
Similarly, when paired, EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) and VAN (Value-Added Network) solutions create a synergy that drives operational excellence and seamless connectivity for your business.
You might be wondering, “How exactly does this partnership work?”
Well, as we just explored, EDI is the backbone of automated data exchange, while a VAN provides the secure, reliable infrastructure needed to ensure every transaction is delivered accurately and efficiently. Together, they form a powerhouse solution to modernize and streamline your supply chain.
Key Takeaways
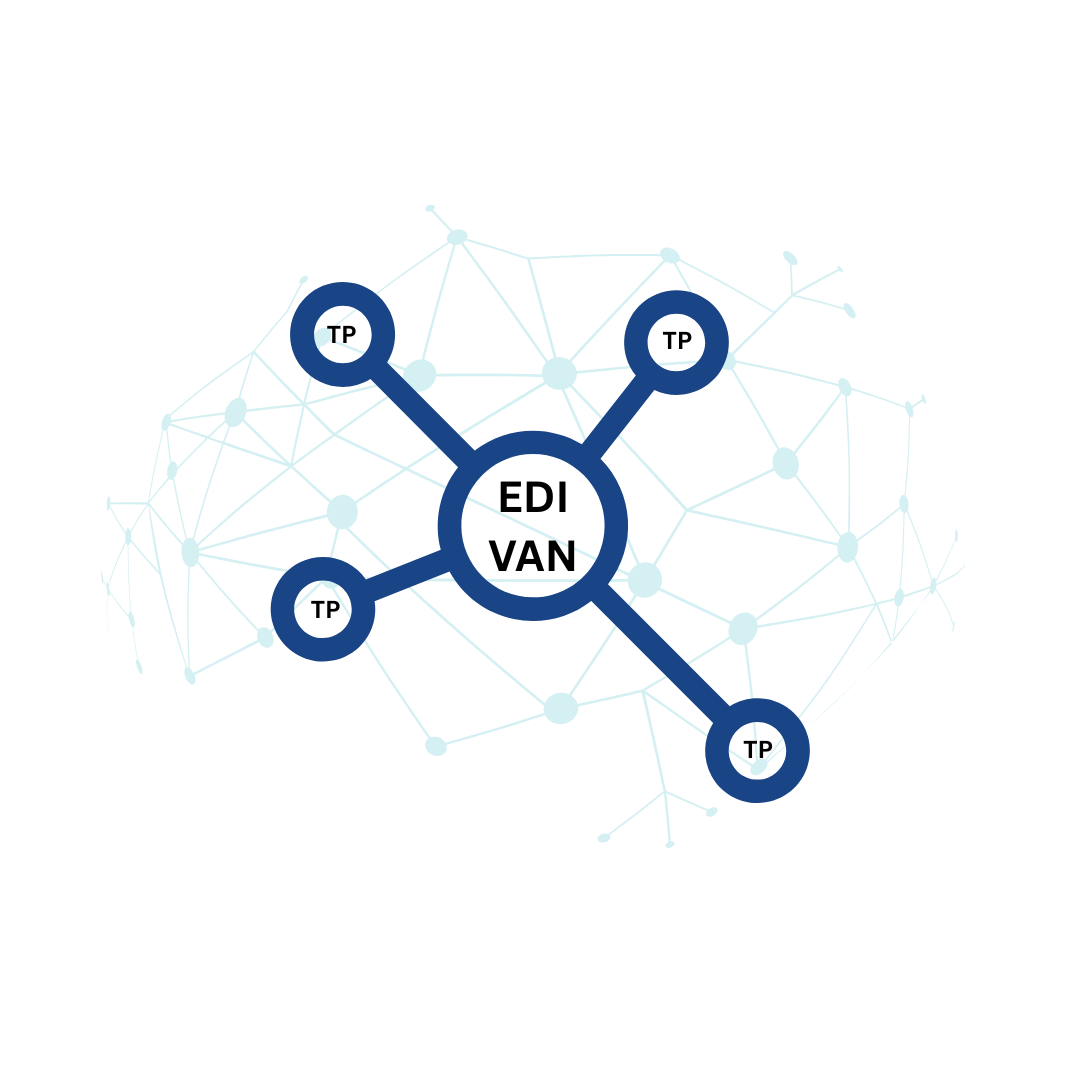
- EDI VAN (Value-Added Network) is a secure, private network for exchanging EDI documents between trading partners.
- It ensures data encryption, reliable delivery, and compliance with EDI standards.
- VANs provide features like message tracking, archiving, and translation services, simplifying EDI management.
- They reduce the complexity of maintaining direct connections with multiple trading partners.
- Choosing a reliable VAN helps businesses streamline operations, improve accuracy, and maintain secure communication.
What is EDI?
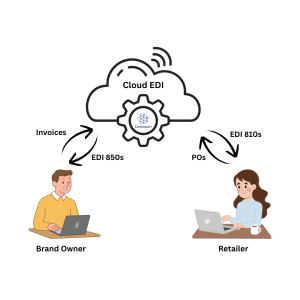
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is the automated exchange of standardized business documents between trading partners. It replaces traditional paper-based processes with electronic transactions, improving speed, accuracy, and efficiency.
Examples of Common EDI Documents
Key Benefits of EDI
- Reduces manual errors
- Speeds up transaction processing
- Enhances supply chain visibility
- Improves collaboration with trading partners
What is a VAN Network?
A Value-Added Network (VAN) is a private, secure communication channel designed to transmit EDI documents between businesses. It acts as a centralized hub, managing the routing, delivery, and acknowledgment of electronic files.
Why “Value-Added”?
The “value-added” aspect comes from additional features such as:
- Data translation and mapping
- Security enhancements
- Protocol conversions
- Archiving and tracking capabilities
The rise of electronic data interchange (EDI) in the late 20th century marked a significant turning point for business communications. As companies sought faster and more secure methods to exchange information, the Value-Added Network (VAN) emerged as a revolutionary solution. VANs are private networks that facilitate the electronic transfer of data between organizations, acting as intermediaries that streamline communication processes. They allow businesses to connect with multiple trading partners through a centralized hub, eliminating the need for costly point-to-point connections.
VANs provide a variety of services that enhance the efficiency of EDI, including data translation, formatting, and storage. This means that businesses no longer need to invest in developing their communication protocols or formats for data exchange. Instead, they can leverage the capabilities of a VAN to standardize the information being transmitted, ensuring compatibility and reducing errors. As a result, organizations can quickly send and receive documents such as purchase orders, invoices, and shipping notices, significantly speeding up their operations.
The emergence of VANs also addressed security concerns associated with traditional methods. By utilizing encryption and secure transmission protocols, VANs offered a more secure environment for exchanging sensitive information. This advancement not only mitigated the risk of data breaches but also instilled greater confidence in businesses to adopt electronic communication methods. As a result, VANs became an integral part of the EDI landscape, revolutionizing the way companies communicated and conducted transactions.
VAN Connection Types
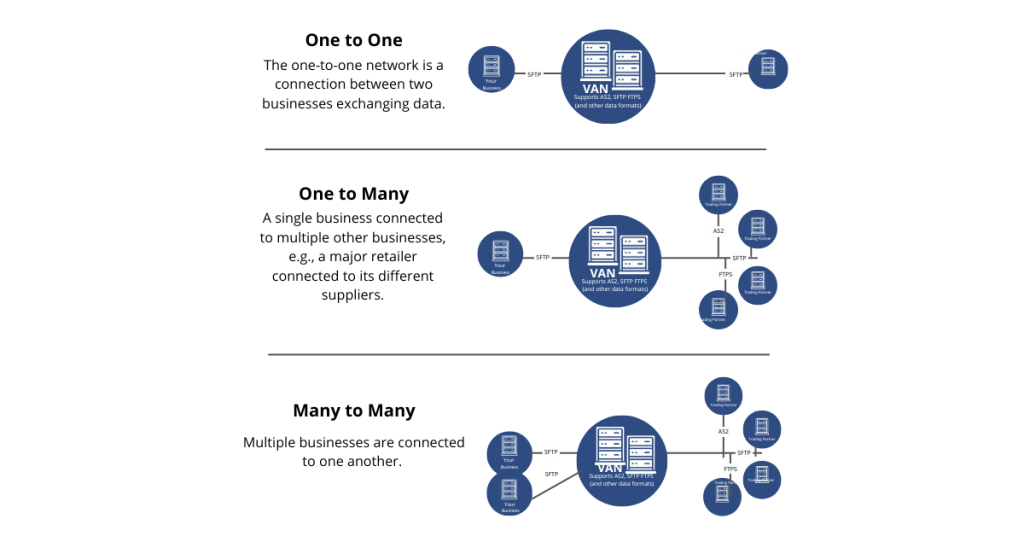
1. One-to-One
The one-to-one network is a direct point-to-point connection between two businesses to exchange EDI data. In this type of network, there is a direct connection between two nodes, and value is added to the information that is transmitted between them.
Example
A peer-to-peer network is where two devices are connected directly to each other for the purpose of sharing files or resources. In this case, value is added by enabling the devices to communicate with each other without the need for a central server or intermediary.
2. One-to-Many
As the name says, a single business is connected to multiple businesses to exchange EDI data.
Example
A single supplier connected to multiple trading partners using a third-party VAN. No matter which communication protocol is used at the trading partner end, VAN can easily connect and transmit the EDI data.
3. Many-to-Many
In this type of setup, multiple businesses are connected. This is the most common type of VAN network connection majorly used in the healthcare, finance, and logistics industries as there are many segments connected to each other via a single destination node.
Different Types of VAN Networks
- Traditional VANs: These are the original type of VANs that have been in use for many years. They provide a wide range of services, such as data validation, formatting, encryption, and communication protocols, to ensure secure and reliable EDI transactions between trading partners.
- Cloud-based VANs: These VANs are hosted on cloud platforms and provide EDI services over the internet. They offer scalable, flexible, and cost-effective solutions for businesses, as they eliminate the need for on-premises hardware and software and provide on-demand resources for processing EDI transactions.
- Integrated VANs: These VANs are integrated with other business systems, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems or Warehouse Management Systems (WMS). They enable seamless integration of EDI transactions with internal business processes, enhancing automation and efficiency.
- Industry-specific VANs: Some VANs are tailored for specific industries or verticals, providing specialized services and compliance with industry-specific EDI standards and regulations. Examples include VANs for healthcare, retail, automotive, and logistics industries.
- Global VANs: These VANs have a global presence and provide EDI services for international trading partners, enabling global supply chain integration and facilitating EDI transactions across borders.
- Managed service provider VANs: These VANs are offered by managed service providers (MSPs) who provide end-to-end management of EDI transactions for businesses, including VAN connectivity, mapping, data validation, and other value-added services, relieving businesses of the burden of managing their own EDI infrastructure.
- Hybrid VANs: Hybrid VANs combine the benefits of both traditional and cloud-based VANs. They offer the security and reliability of traditional VANs, while also providing flexibility and scalability of cloud-based VANs. Hybrid VANs are ideal for businesses that require a high level of security for their data but also need to be able to quickly adapt to changing business needs. They can also be customized to meet specific business requirements, such as integrating with legacy systems or providing advanced analytics and reporting.
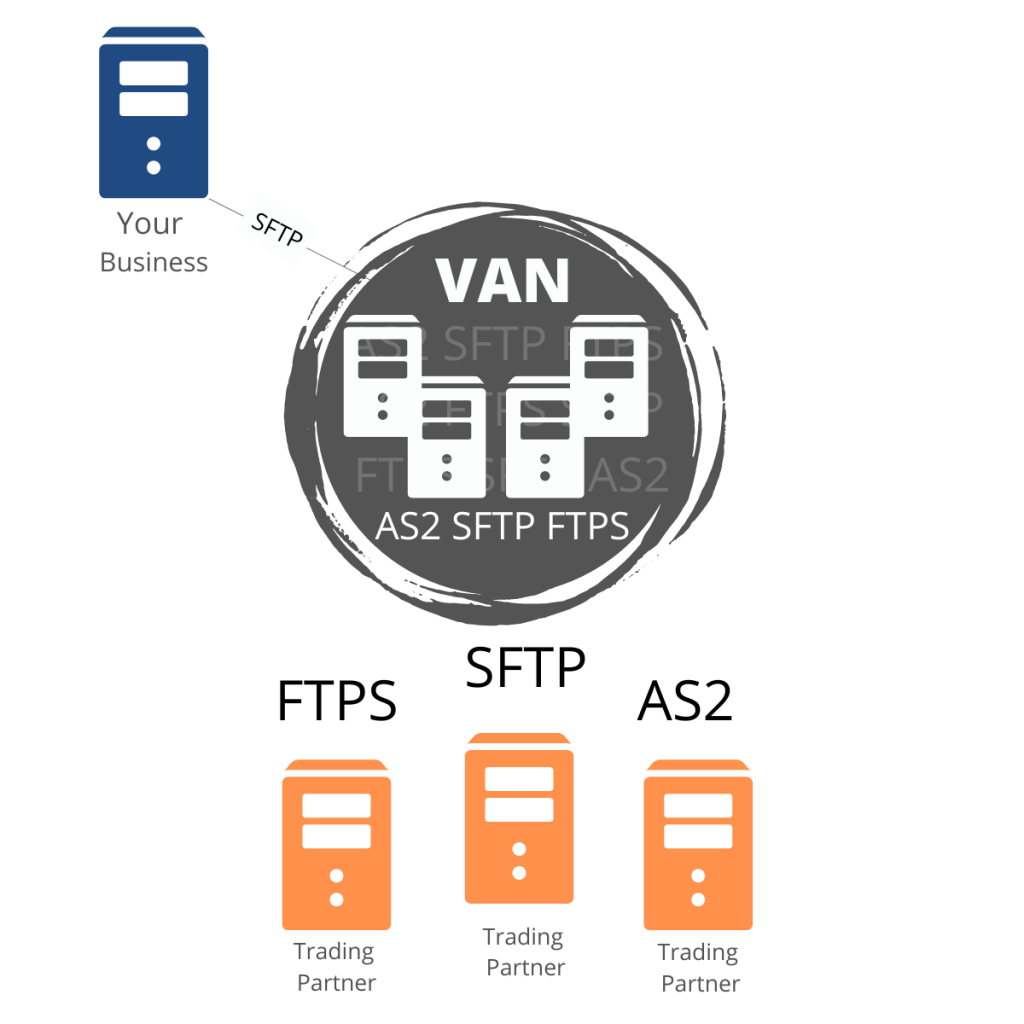
Common Communication Protocols Supported by a VAN
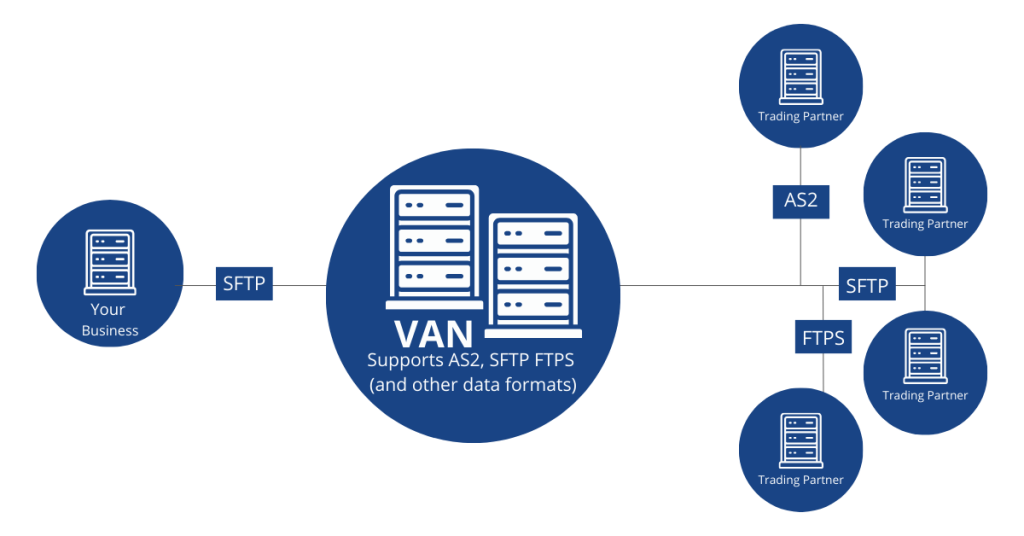
VANs support multiple communication protocols to ensure compatibility with diverse systems.
- AS2 (Applicability Statement 2)
- Direct, point-to-point connection.
- Highly secure and widely adopted in retail.
- sFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol)
- Ensures encrypted file transfer between systems.
- HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure)
- Uses web-based connections for secure data exchange.
- FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
- Basic file transfer method, less secure but widely used.
- X.400
- Messaging protocol for document exchange, common in Europe.
How VAN Helps Streamline Your Communication With Trading Partners
VANs simplify EDI communication in several ways:
- Centralized Routing: All transactions are routed through the VAN, ensuring efficient delivery.
- Protocol Conversion: Translates data into compatible formats for seamless communication.
- Data Validation: Checks transactions for errors before delivery.
- Tracking and Monitoring: Provides real-time visibility into the status of transactions.
- Compliance Management: Ensures adherence to industry-specific standards like HIPAA or GS1.
Sending and Receiving EDI Transactions Using VAN
Once you have set up your Value Added Network (VAN) and established a connection with your VAN service provider, you can start sending and receiving Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) transactions using the VAN. Here are the general steps for sending and receiving EDI transactions via VANs:
Sending EDI Transactions Via VAN
Prepare EDI Data:
Prepare your EDI data according to the EDI standards and specifications required by your trading partners. This may involve generating EDI messages using EDI software or converting your business data into EDI format
Connect to the VAN:
Establish a connection to your VAN service provider using the communication protocols and methods agreed upon during the VAN setup process. This may involve using protocols such as FTP (File Transfer Protocol), AS2 (Applicability Statement 2), or other communication methods supported by the VAN service provider.
Transmit EDI Data:
Transmit the prepared EDI data to the VAN service provider using the agreed-upon communication method. This may involve uploading the EDI data to a designated folder on the VAN’s FTP server, sending the data as an email attachment using AS2, or using other methods supported by the VAN service provider.
VAN Processing:
The VAN service provider receives the transmitted EDI data and performs VAN-specific processing, such as validating the EDI syntax, translating the EDI data into the appropriate format required by the recipient, and performing data integrity checks.
Routing and Delivery:
The VAN routes the EDI data to the appropriate recipient based on the trading partner information provided during the setup process. The VAN may use routing information, such as EDI headers, envelopes, or other VAN-specific routing mechanisms, to ensure that the data is delivered to the correct recipient.
Receiving EDI Transactions via VAN
VAN Processing:
When your trading partner sends an EDI transaction to you via the VAN, the VAN receives and processes the transaction. This may involve VAN-specific processing, such as validating the EDI syntax, performing data integrity checks, and translating the EDI data into the appropriate format for your system.
Notification:
Once the EDI transaction is successfully processed by the VAN, you may receive a notification, such as an email or a system alert, indicating that you have new EDI data available for retrieval.
Retrieval of EDI Data:
Retrieve the EDI data from the VAN using the agreed-upon communication method, such as downloading the data from a designated folder on the VAN’s FTP server or receiving the data as an email attachment using AS2.
EDI Data Integration:
Integrate the received EDI data into your business system, such as your ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system, accounting system, or other relevant applications. This may involve using EDI software or other integration tools to convert the EDI data into a format that can be processed by your system.
Processing and Acknowledgment:
Process the received EDI data according to your business rules and requirements. Generate acknowledgments, such as EDI functional acknowledgments (997s) or other acknowledgment messages, to inform your trading partners about the status of the transactions received.
It is important to work closely with your VAN service provider to understand their specific processes, protocols, and requirements for sending and receiving EDI transactions. Ensure that you follow the agreed-upon communication methods, data formats, and security measures to ensure smooth and secure EDI transactions via VANs.
Benefits of Using VAN Over Other Communication Protocols
- Enhanced Security
VANs use encryption and authentication to protect sensitive data.
- Simplified Integration
Centralized routing and protocol support make integration seamless.
- Scalability
Handles large transaction volumes effortlessly.
- Reduced IT Burden
VAN providers manage infrastructure, maintenance, and upgrades.
- Improved Visibility
Track transactions in real-time and access historical data for audits.
Why Choose Commport VAN as Your EDI VAN Provider?
Commport Communications stands out as a trusted VAN provider with decades of expertise.
Key Features of Commport VAN
- Comprehensive Protocol Support: AS2, sFTP, HTTPS, and more.
- Inbuilt Translation and Mapping: Simplifies EDI implementation.
- Data Security: Ensures compliance with international standards.
- Scalability: Supports businesses of all sizes, from SMEs to large enterprises.
- 24/7 Support: Dedicated customer service to address your needs.
By choosing Commport, businesses can enjoy a reliable and efficient VAN solution tailored to their unique requirements.
Conclusion
A Value-Added Network (VAN) is a game-changer in EDI communication, providing secure, efficient, and scalable solutions for businesses. From protocol conversion to real-time tracking, VANs simplify the complexities of electronic document exchange, empowering organizations to focus on growth.
With Commport Communications as your VAN provider, you can unlock the full potential of EDI and streamline your supply chain operations. Embrace VAN technology today to stay ahead in the competitive business landscape.
Commport VAN Network
Download: VAN Buyers Guide
Maximize your business efficiency with the right VAN provider! Grab your free VAN Buyer's Guide and discover the key features and services that will elevate your EDI transactions to the next level.
Make an informed decision today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, many VAN providers offer inbuilt EDI translation and mapping capabilities.
- Translation: Converts raw EDI data into readable formats (e.g., XML or CSV).
- Mapping: Aligns data fields between different systems to ensure compatibility.
These features eliminate the need for additional software, reducing costs and complexity.
When selecting a VAN provider, consider:
- Protocol and industry-standard compliance
- Scalability and flexibility
- Security measures
- Additional features like data translation and tracking
- Customer support availability
Commport Communications offers all these benefits, making it a leading choice for VAN services.
VANs use advanced encryption, authentication protocols, and secure communication methods like AS2 and sFTP to ensure data security. They also provide audit trails and compliance with regulations like GDPR, or GS1 standards.
Yes, small businesses can greatly benefit from using a VAN. It eliminates the need for expensive infrastructure, simplifies compliance with trading partner requirements, and offers scalability as the business grows.
While direct connections like AS2 establish a point-to-point link between partners, a VAN acts as a centralized hub for all communications. A VAN provides additional features like protocol conversion, transaction tracking, and data validation, making it a more comprehensive solution.