Introduction
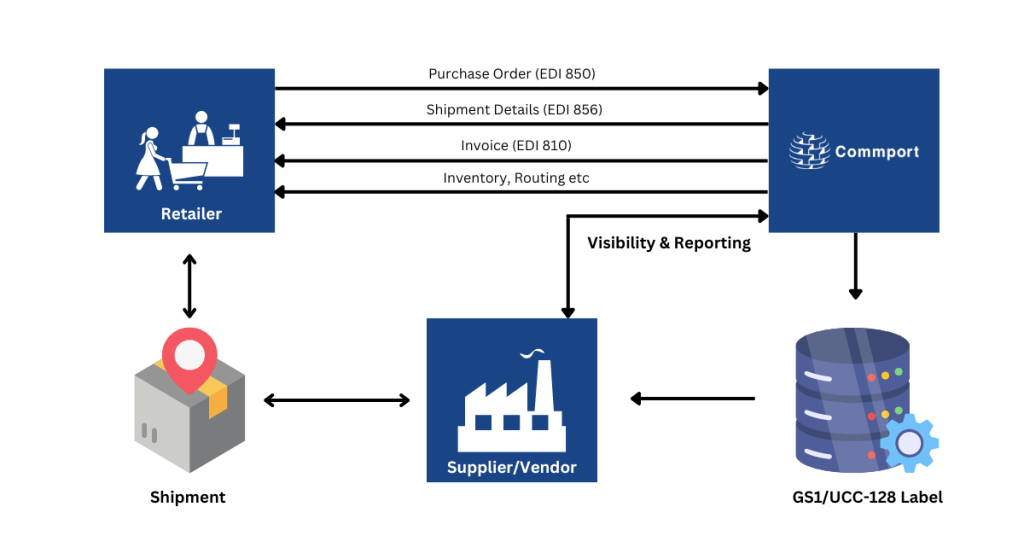
The retail industry uses EDI in 3 stages,
- Procurement
- Shipping
- Invoicing
1. Procurement
Procurement is the method of purchasing goods or services, typically for business purposes. During the procurement process, the retail industry uses EDI to exchange purchase orders (EDI 850) and purchase order acknowledgments (EDI 855). The buyer/retailer sends a purchase order to the supplier and the supplier then sends the purchase order acknowledgment back to the buyer/retailer.
2. Shipping
Logistics/shipping plays a big part in the retail supply chain. In this stage, the supplier sends the advance ship notice (EDI 856) to the buyer/retailer. The advance ship notice (ASN) provides the buyer with information like what is being sent in each package when it’ll be sent, by whom, and more. ASN plays a very important role can helping retailers relieve stock congestion and reduce check-in times.
“According to the research from the Grocery Manufacturers of America, ASNs slash receiving times by up to 60% if just one part of deliveries uses automated ASNs, a 250-store company can save 65,000 receiving hours each year.”
The ASN can ensure that every step of the supply chain is fully informed of the status of the goods.

3. Invoicing
In the final stage, the supplier issues an EDI invoice (EDI 810) to request payments for products delivered. EDI 810 document consists of invoice details like invoice number, date, shipping details, payment terms, and item information like information including prices and quantities, discounts, and more. To this, the retailer will respond with EDI remittance advice (EDI 820) and send it to the supplier to confirm payment
Benefits of EDI in the Retail Industry
1. Reduce transaction times
In contrast to the manual paper-based system, EDI messages can be exchanged in seconds, which leads to faster invoice processing and improved cash flows. By using EDI solutions buyers/retailers can receive EDI invoices directly into their accounting software so they can process them quickly and efficiently.
2. Reduce costly errors, avoid delays, and save costs
Manual processing is prone to Invoicing errors and can be costly leading to chargebacks from retailers. Also, errors in documents can cause delays in shipments and goods receivable disrupting the supply chain. However, by using an effective EDI solution you can reduce all these costly errors, improve operational efficiency, and save thousands of dollars.
3. Expand your fulfillment Models
Support eCommerce growth and create a seamless consumer experience across channels using standardized EDI transactions.
4. Simply order management and improve warehouse efficiency
Get EDI order information from suppliers and gain visibility into whether suppliers can fulfill orders in full and on time. By receiving automated ASNs from suppliers you can move your inventory efficiently through your supply chain and plan better warehouse management, which in turn improves warehouse operational efficiency.
5. Automation
With EDI you can automate your entire supply chain cycle. From procurement, shipping, and order management. Onboarding your suppliers to EDI will enable a consistent order fulfillment process.
6. Improve supplier efficiency
EDI can help retailers gain visibility into order management which means which suppliers are delivering orders on time, correctly, and quickly and which are not. With this type of data, retailers can make changes if certain suppliers just aren’t cutting it. This type of insight would take months to discover without an EDI system.
7. Effective product management and bust trends
Gain visibility into product performance. EDI can help retailers help identify trending products i.e., which products are selling like hotcakes, and which are not. This will help retailers adjust inventory supplies accordingly.
8. Increase sales with drop shipping
Drop shipping is a process of providing goods directly from manufacturers to retailers or customers. If a retailer provides an option to its customers to order products online via its eCommerce store, instead of storing the inventory in the retailer warehouse, with the help of EDI it can send the same order information to its supplier and ask the supplier to fulfill the order directly to its customer from their warehouse. In this way, retailers can save time and storage space by not storing the inventory and processing orders faster for its customers. All this can happen with an effective EDI system.
Conclusion
The integration of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) in the retail industry has proven to be a game-changer, revolutionizing the way business transactions occur. By facilitating the electronic exchange of critical documents like purchase orders, invoices, and shipping notices, EDI streamlines supply chain processes, reduces operational costs and enhances overall efficiency.
As the retail landscape continues to evolve, EDI stands as a catalyst for improved communication, faster order fulfillment, and the creation of a more agile and interconnected retail ecosystem. Its impact extends beyond individual transactions, fostering collaborative relationships between retailers, suppliers, and other stakeholders, ultimately contributing to a more responsive and competitive retail environment.
EDI X12 Transaction | EDI Transaction Name / Document Type | |
EDI 180 | Return Merchandise Authorization and Notification | Read More |
EDI 290 | Cooperative Advertising Agreements | Read More |
EDI 810 | Invoice | Read More |
EDI 816 | Organizational Relationships | Read More |
EDI 832 | Price/Sales Catalog | Read More |
EDI 846 | Inventory Inquiry/Advice | Read More |
EDI 850 | Purchase Order | Read More |
EDI 855 | Purchase Order Acknowledgment | Read More |
EDI 856 | Ship Notice/Manifest | Read More |
EDI 857 | Shipment and Billing Notice | Read More |
EDI 860 | Purchase Order Change Request – Buyer Initiated | Read More |
EDI 865 | Purchase Order Change Acknowledgement/Request – Seller Initiated | Read More |
EDI 869 | Order Status Inquiry | Read More |
EDI 870 | Order Status Report | Read More |
EDI 875 | Grocery Product Purchase Order | Read More |
EDI 876 | Grocery Products Purchase Order Change | Read More |
EDI 877 | Manufacturer Coupon Family Code Structure | Read More |
EDI 880 | Grocery Products Invoice | Read More |
EDI 881 | Manufacturer Coupon Redemption Detail | Read More |
EDI 885 | Retail Account Characteristics | Read More |
EDI 887 | Coupon Notification | Read More |
EDI 888 | Item Maintenance | Read More |
Ready to find out more about Commport EDI Solutions?
Need Help? Download: EDI Buyers Guide
Unlock the full potential of your supply chain with our comprehensive EDI Buyer's Guide — your first step towards seamless, efficient, and error-free transactions
Frequently Asked Questions
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is a standardized electronic communication method for exchanging business documents between trading partners. In the retail industry, EDI plays a crucial role in automating and streamlining various processes, such as order placement, inventory management, shipping, and invoicing.
EDI streamlines order processing by enabling automated communication between retailers and suppliers. Retailers can send electronic purchase orders (POs) directly to suppliers, who can then confirm and acknowledge receipt electronically. This minimizes manual data entry, reduces errors, and accelerates the order-to-fulfillment cycle.
Yes, EDI enhances inventory management by providing real-time visibility into stock levels, reorder points, and demand forecasts. Retailers can share accurate inventory data with suppliers, allowing for just-in-time restocking and minimizing stockouts. EDI also supports advanced shipping notices (ASNs), notifying retailers about incoming shipments and aiding in efficient inventory planning.
EDI facilitates the exchange of product information, pricing, and catalog updates between retailers and suppliers. Retailers can receive electronic product catalogs, update pricing information, and introduce new products seamlessly. This ensures that accurate and up-to-date product details are readily available for consumers, both in physical stores and online.
EDI offers numerous benefits for retail partners and the supply chain. It reduces manual data entry, minimizes errors, enhances order accuracy, shortens order-to-cash cycles, and improves collaboration between retailers and suppliers. By automating processes, EDI increases operational efficiency, lowers costs, and enables faster response to market demands.