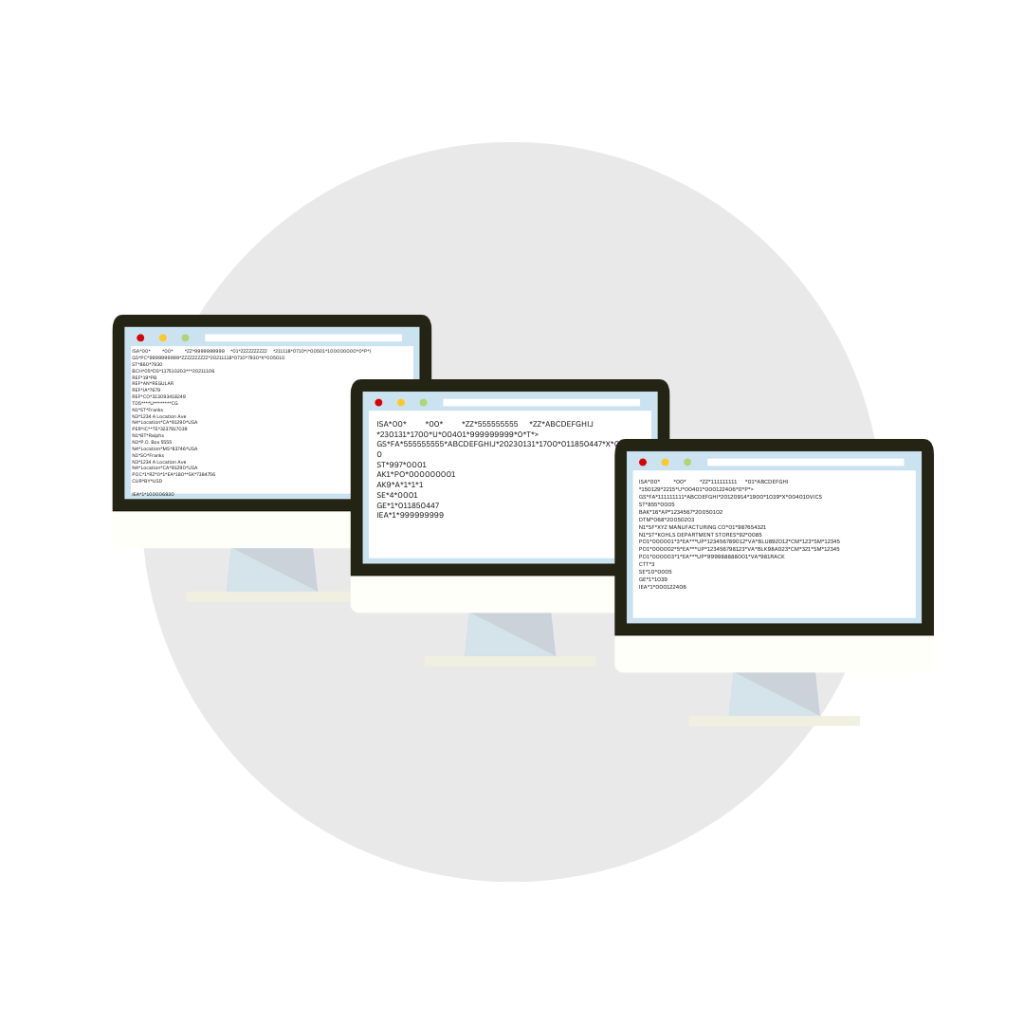
- Shipment Number
- Shipping Date
- Expected delivery date
- Ship from/to addresses and information
- Purchase order number
- Item details and quantities
- Shipment tracking details (BOL Number, PRO Number, Tracking Number)
- Item tracking details where applicable
- Packaging detail (carton, pallet level details)
- UCC128/GS1 Numbers
Sending the EDI 856
An EDI translator is needed to generate the EDI 856 ship notice/manifest, once the ASN is created, it is then sent to the recipient through some form of electronic communication. There are many types of EDI, sending an EDI 856 the issuer can use one of many, most commonly through a Value Added Network (VAN) or through an EDI cloud service.
Value Added Networks receives an EDI 856 from a sender, and sorts and delivers it to the recipient’s mailbox. The recipient retrieves messages by connecting to the VAN, which validates the message and verifies the recipient’s identity. It then provides a full audit trail, and all messages are tracked and accurately recorded
Sending the EDI 856 directly to the recipient using the Internet as the communication standard. Typically done through software that can send the EDI 856 using a method known as AS2. When using AS2 to send the EDI 856, the document is encrypted at the source and is sent using secured Internet-based communication to the recipient, which must then have software capable of decrypting the EDI 856.
Translating the EDI 856
Once the recipient has successfully received and decrypted the EDI 856, the next step is to translate it into a format that is more readily available.
1. Human readable form of the EDI 856 that is easily understood by the reader.
2. Flat-file form that is easily sent to the recipient’s computer system. This is typically an ERP or accounting system form.
This form of EDI translation is also known as integrated EDI