There are different types of value added networks that offer various services to meet the needs of different industries and businesses.
Introduction
A Value Added Network (VAN) is a private network that facilitates secure data transmission of EDI files between trading partners. Some 3rd party VAN providers also provide additional services such as data validation, formatting, encryption, and communication protocols to ensure the secure and reliable transmission of data.
Some VAN providers also offer other value-added services, such as data mapping, data transformation, and other customization options, to meet specific business requirements. VANs have gained the trust of many businesses and serve as a secure and efficient data transmission protocol to exchange EDI documents, such as purchase orders, invoices, shipping notices, and more with their trading partners, enabling seamless integration of supply chains and enhancing business processes & efficiency.
Key Takeaways
- Value-Added Networks (VANs) are private networks used to securely exchange EDI documents between businesses.
- There are different types of VANs, including:
- Industry-Specific VANs: Tailored to meet the needs of specific sectors like retail, healthcare, or logistics.
- Global VANs: Designed for businesses with international operations, supporting multi-language and multi-standard transactions.
- Customizable VANs: Allow businesses to integrate specific features for unique requirements.
- VANs provide services like data encryption, message tracking, and compliance with EDI standards.
- Choosing the right type of VAN depends on the size, scope, and specific needs of your business operations.
How Value Added Network (VAN) Works?
When companies and their trading partners need to communicate, they typically connect to the same value-added network (VAN), which is often outsourced to an EDI VAN provider. Once all parties are connected to the VAN, any EDI documents they send to each other will pass through the VAN before reaching their intended recipients. The VAN may also handle any necessary translation of the EDI documents to ensure they arrive in the correct format.
Businesses often utilize value-added networks to enhance the efficiency of their supply chain management with suppliers. VAN works in a mailbox setting, companies transmit transactions to a VAN, which then delivers them to the receiver’s mailbox. The receiver retrieves the transaction by contacting the VAN and subsequently sends the transaction. Although the system shares similarities with email, it primarily serves as a means for transmitting standardized, structured data rather than unstructured text. There are also many other benefits of VAN across various industries.
Market Stats About Value Added Network
- Market Size: According to a report by Market Research Future, the global Value Added Network (VAN) market was valued at USD 1.73 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach USD 3.51 billion by 2027, with a CAGR of 10.3% during the forecast period (2021-2027). [Reference: Market Research Future – Value Added Network (VAN) Market Report]
- Adoption of Cloud-based VANs: Cloud-based VANs are gaining popularity due to their scalability, flexibility, and cost-effective nature. According to a report by Allied Market Research, the global cloud-based VAN market is expected to reach USD 4.92 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 11.3% from 2020 to 2027. [Reference: Allied Market Research – Cloud-based Value Added Network (VAN) Market Report]
Value Added Network (VAN) Connection Types
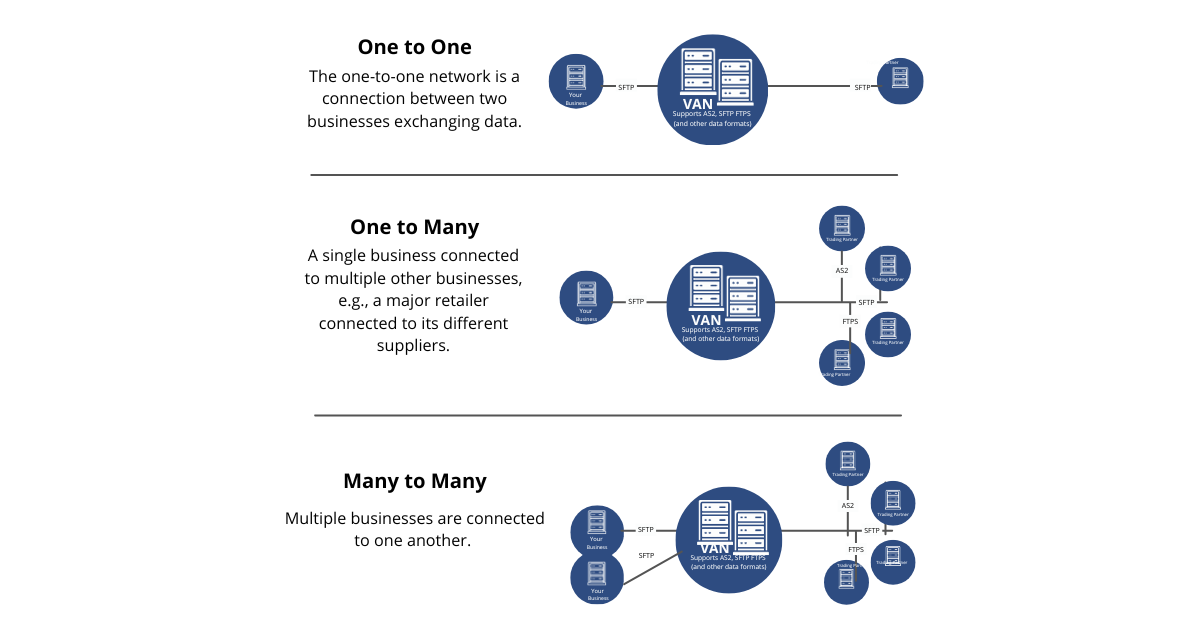
1. One-to-One
The one-to-one network is a direct point-to-point connection between two businesses to exchange EDI data. In this type of network, there is a direct connection between two nodes, and value is added to the information that is transmitted between them.
Example
A peer-to-peer network is where two devices are connected directly to each other for the purpose of sharing files or resources. In this case, value is added by enabling the devices to communicate with each other without the need for a central server or intermediary.
2. One-to-Many
As the name says, a single business is connected to multiple businesses to exchange EDI data.
Example
A single supplier connected to multiple trading partners using a third-party VAN. No matter which communication protocol is used at the trading partner end, VAN can easily connect and transmit the EDI data.
3. Many-to-Many
In this type of setup, multiple businesses are connected. This is the most common type of VAN network connection majorly used in the healthcare, finance, and logistics industries as there are many segments connected to each other via a single destination node.
Here is the List of 9 Different Types of Value Added Networks
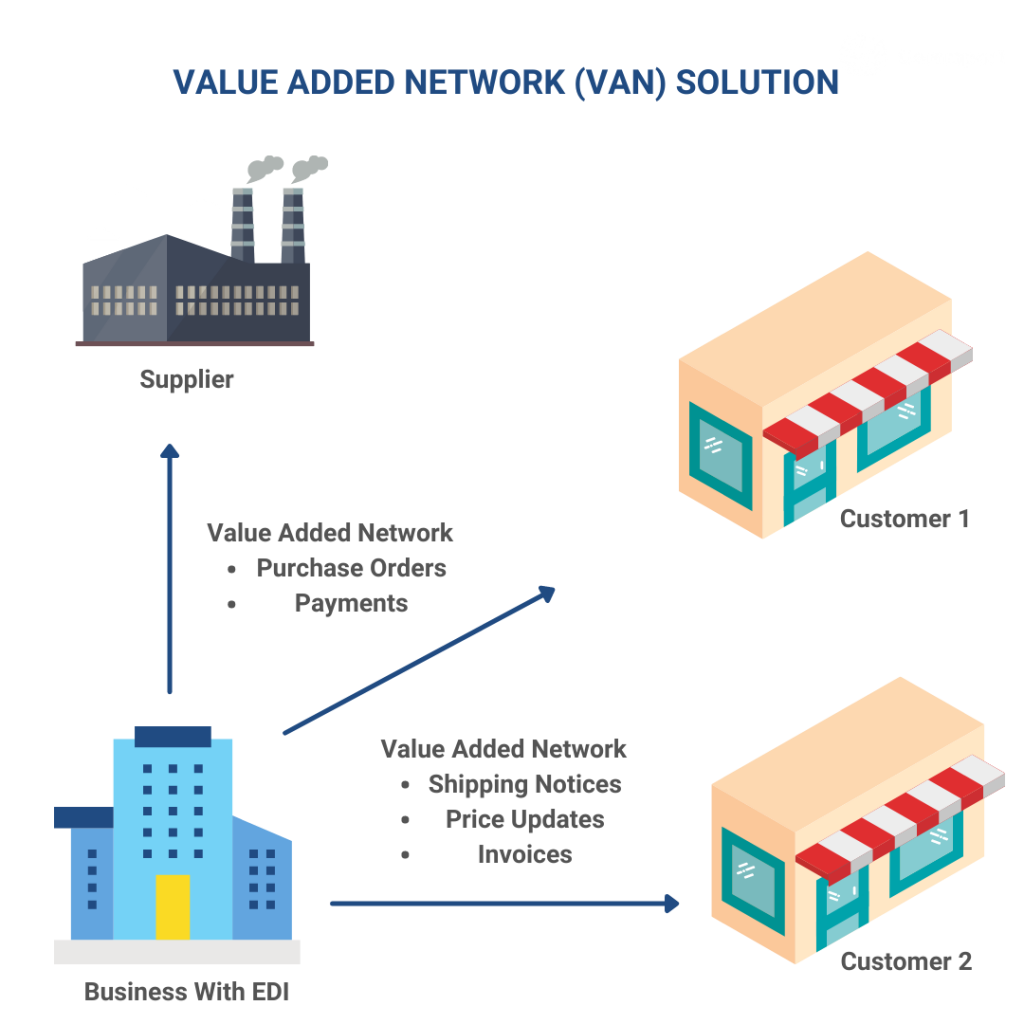
Value-added networks (VANs) are a crucial component of modern business communication, allowing companies to exchange electronic data in a secure and efficient manner. There are many different types of Value Added Networks (VANs) available, each with its own unique features, services, and benefits, catering to the diverse needs of businesses across various industries and geographies. In this blog, we’ll explore the different types of VANs and help you choose the right one for your business needs.
- Traditional VANs: These are the original type of VANs that have been in use for many years. They provide a wide range of services, such as data validation, formatting, encryption, and communication protocols, to ensure secure and reliable EDI transactions between trading partners.
- Internet-based VANs: Also known as Web-based VANs or Web EDI, these VANs leverage the internet as the communication medium for EDI transactions. They provide web-based interfaces that allow businesses to access and manage their EDI transactions through a web browser, making them more accessible and convenient.
- Cloud-based VANs: These VANs are hosted on cloud platforms and provide EDI services over the internet. They offer scalable, flexible, and cost-effective solutions for businesses, as they eliminate the need for on-premises hardware and software and provide on-demand resources for processing EDI transactions.
- Integrated VANs: These VANs are integrated with other business systems, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems or Warehouse Management Systems (WMS). They enable seamless integration of EDI transactions with internal business processes, enhancing automation and efficiency.
- Industry-specific VANs: Some VANs are tailored for specific industries or verticals, providing specialized services and compliance with industry-specific EDI standards and regulations. Examples include VANs for healthcare, retail, automotive, and logistics industries.
- Value-added service provider VANs: These VANs are offered by value-added service providers (VASPs) who specialize in providing additional services on top of basic VAN services. These services may include data mapping, data transformation, data validation, and other value-added services to meet specific business requirements.
- Global VANs: These VANs have a global presence and provide EDI services for international trading partners, enabling global supply chain integration and facilitating EDI transactions across borders.
- Managed service provider VANs: These VANs are offered by managed service providers (MSPs) who provide end-to-end management of EDI transactions for businesses, including VAN connectivity, mapping, data validation, and other services, relieving businesses of the burden of managing their own EDI infrastructure.
- Hybrid VANs: Hybrid VANs combine the benefits of both traditional and cloud-based VANs. They offer the security and reliability of traditional VANs, while also providing the flexibility and scalability of cloud-based VANs. Hybrid VANs are ideal for businesses that require a high level of security for their data but also need to be able to quickly adapt to changing business needs. They can also be customized to meet specific business requirements, such as integrating with legacy systems or providing advanced analytics and reporting.
Conclusion
Value Added Networks (VANs) play a critical role in facilitating electronic data interchange (EDI) between businesses. There are different types of VANs that offer various services to meet the needs of different industries and businesses. Choosing the right type of VAN depends on the business’s size, industry, and EDI needs. Understanding the differences between the various types of VANs is crucial in selecting the most suitable one for your business.
Want to learn more about VAN?
Here is the complete guide to value added network
Ready to find out more about Commport Value Added Network?
Download: VAN Buyers Guide
Maximize your business efficiency with the right VAN provider! Grab your free VAN Buyer's Guide and discover the key features and services that will elevate your EDI transactions to the next level.
Make an informed decision today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Value Added Networks (VANs) are secure and reliable platforms that facilitate electronic data interchange (EDI) between business partners. There are several types of VANs available, including public VANs, private VANs, cloud-based VANs, industry-specific VANs, and hybrid VANs. Each type offers unique features and benefits tailored to different business needs.
A Public Value Added Network is a VAN that serves a wide range of businesses across various industries. It offers a shared platform for EDI communication, making it cost-effective for small to medium-sized businesses with moderate transaction volumes. Public VANs are suitable when businesses require broad connectivity, standard document exchange, and affordability.
A Private Value Added Network is a dedicated network established for a specific organization or group of partners. Unlike public VANs, private VANs offer enhanced security, customization, and control over data exchange processes. This type of VAN is suitable for larger enterprises or organizations that demand heightened security and require tailored integration with internal systems.
A Cloud-based Value Added Network operates on cloud infrastructure, offering scalability, flexibility, and accessibility. It allows businesses to scale their EDI operations seamlessly, adapt to changing business needs, and access the network from anywhere with an internet connection. Cloud-based VANs are particularly beneficial for businesses looking for rapid deployment and reduced IT maintenance.
Industry-specific Value Added Networks cater to the needs of a particular industry, such as healthcare, automotive, retail, or logistics. These VANs often come with preconfigured templates, document formats, and compliance standards tailored to the specific industry’s requirements. They streamline EDI processes and ensure adherence to industry standards, making them highly beneficial for businesses operating within specialized sectors.
Remember that choosing the right type of Value Added Network depends on factors such as business size, transaction volume, security requirements, industry regulations, and integration needs. It’s important to evaluate your organization’s specific needs before selecting a VAN type.