Introduction
Accounting is often called the language of business because it provides a structured way to record, analyze, and communicate financial information.
Whether you’re a small business owner managing daily transactions, a corporate executive analyzing profits, or an investor evaluating opportunities, accounting provides the insights needed to drive success.
With various branches like
- financial accounting,
- managerial accounting,
- tax accounting, and auditing,
this field serves diverse purposes across industries.
At its core, accounting involves tracking income, expenses, assets, and liabilities to generate accurate financial statements.
These statements—
- such as the balance sheet,
- income statement,
- and cash flow statements
help stakeholders like investors, management, and regulators assess financial performance and make informed decisions.
With a lot of data and manual work things can go wrong easily. This is where an automated and standardized data management solutions like EDI can help.
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) has emerged as a game-changing technology, revolutionizing how companies handle their accounting processes. By automating data exchange and streamlining financial workflows, EDI is transforming the landscape of modern accounting.
EDI can directly integrate with existing financial software, creating a cohesive ecosystem for managing financial data. By standardizing document formats and automating data exchange, EDI ensures consistency, reduces errors, and accelerates financial processes. This technological advancement is particularly valuable in today’s global business landscape, where speed and accuracy in financial transactions are critical for maintaining a competitive edge.
The Evolution of Financial Data Exchange

The journey from traditional paper-based accounting to modern EDI systems represents a significant leap in financial management practices. Historically, businesses relied on manual processes, which were prone to errors, delays, and inefficiencies. The advent of EDI has transformed this landscape, offering a more streamlined and error-free approach to handling financial data.
In the early days of computerization, financial data was often exchanged via email or basic file transfers. While this was an improvement over paper-based systems, it still lacked the standardization and automation that modern businesses require. EDI emerged as a solution to these challenges, providing a structured format for data exchange that could be easily integrated into various accounting systems.
Today, EDI has evolved to incorporate advanced features such as real-time data processing, cloud-EDI based solutions, and integration with artificial intelligence for predictive analytics. This evolution has not only improved the accuracy and speed of financial transactions but has also opened new possibilities for financial analysis and strategic decision-making.
EDI Integration in Accounting Systems
Integrating EDI into existing accounting systems is a crucial step in modernizing financial processes. This integration allows for seamless data flow between EDI and accounting software, creating a unified ecosystem for financial management.
Steps for Successful EDI Integration
- Assessment of Current Systems: Evaluate existing accounting software and processes to identify integration points and potential challenges.
- Selection of EDI Solution: Choose an EDI solution that aligns with your business needs and is compatible with your current accounting system. Make sure the EDI system directly integrates with your existing accounting software making the entire process automated.
- Mapping and Configuration: Map EDI documents to corresponding fields in your accounting software and configure the system to handle various transaction types.
- Testing and Validation: Conduct thorough testing to ensure accurate data transfer and handling of different scenarios.
- Training and Implementation: Train staff on the new integrated system and implement it in phases to minimize disruption.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Optimization: Regularly review the integrated EDI system’s performance and adjust as needed to optimize efficiency.
Common EDI Standards and Transactions Sets Used in Accounting
EDI transactions for accounting follow globally recognized EDI standards to ensure consistency and interoperability across different financial systems.
The two most popular EDI standards are ANSI X12 and UN/EDIFACT.
ANSI X12 Vs EDIFACT Which one to choose depends on where you do business.
ANSI X12
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) X12 is widely used in North America. It includes specific transaction sets for accounting-related documents such as:
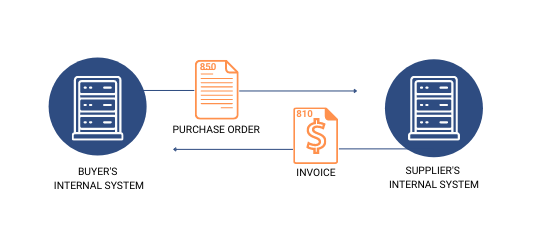
- 810: Invoice
- 820: Payment Order/Remittance Advice
- 850: Purchase Order
UN/EDIFACT
The United Nations Electronic Data Interchange for Administration, Commerce and Transport (UN/EDIFACT) is an international EDI standard. It includes messages for various accounting functions, such as:
- INVOIC: Invoice
- REMADV: Remittance Advice
- ORDERS: Purchase Order
Key Benefits of EDI in Accounting
Implementing EDI in accounting processes offers a multitude of advantages that can significantly enhance a company’s financial operations. Let’s delve into some of the primary benefits:
1. Enhanced Accuracy and Reduced Errors
One of the most significant advantages of EDI in accounting is the dramatic reduction in data entry errors. By automating the transfer of financial information, EDI eliminates the risk of human error associated with manual data input. This increased accuracy leads to more reliable financial records, reduced discrepancies, and fewer disputes with trading partners.
Moreover, EDI systems often include built-in validation checks that can identify and flag potential errors before they enter the accounting system. This proactive approach to error detection helps maintain the integrity of financial data and ensures that decision-makers have access to accurate, up-to-date information.
2. Improved Efficiency and Time Savings
EDI significantly accelerates financial processes by automating data exchange. Tasks that once took hours or days to complete manually can now be executed in minutes. This efficiency gain allows accounting teams to focus on more strategic activities, such as financial analysis and planning, rather than spending time on data entry and reconciliation.
The time savings extend beyond just the accounting department. Faster processing of invoices and payments can improve cash flow management, while quicker order processing can enhance customer satisfaction and streamline supply chain operations.
3. Cost Reduction and Resource Optimization
Implementing EDI can lead to substantial cost savings for businesses. By reducing the need for paper, printing, and manual data entry, companies can significantly lower their operational expenses. Additionally, the reduction in errors and the speed of processing can minimize costly disputes and delays in financial transactions.
EDI also allows for better resource allocation. With routine tasks automated, accounting staff can be redeployed to more value-added activities, maximizing the use of human resources and potentially reducing the need for additional hires as the business grows.
4. Enhanced Compliance and Audit Trails
EDI systems provide robust audit trails for all financial transactions. Every document exchange is logged and timestamped, creating a clear record of all financial activities. This level of documentation is invaluable for compliance purposes, making it easier to adhere to regulatory requirements and conduct internal and external audits.
The standardized format of EDI transactions also ensures consistency across different systems and trading partners, further enhancing compliance and reducing the risk of regulatory issues.
Industry Use Case – Example
Let us take the retail industry as an example, here are some of the key accounting processes that can be automated with the help of EDI within a retail store,
1. Automated Invoice Processing
Almost all retailers use EDI to automate their invoice process. When a supplier sends an electronic invoice via EDI, it is automatically received, validated, and entered into the accounting system. This automation eliminates manual data entry, reduces processing time from days to minutes, and significantly decreases the likelihood of errors.
2. Streamlined Order to Cash Cycle (O2C)
Order to cash also known as O2C is the end-of-end process that businesses follow to receive and process customer orders, deliver goods or services, and collect payments. It is a critical component of the financial supply chain, ensuring smooth revenue generation and cash flow management. EDI can automate each of the steps in this process. This streamlined approach accelerates cash flow and improves financial visibility.
3. Reconciliation of Payments (Accounts Receivable)
Retail stores order products from their suppliers regularly, and when they receive a shipment, the accounting system with an integrated EDI solution can automatically match the EDI 810 (Invoice) with EDI 856 (Advance ship notice) and EDI 850 (purchase order) before releasing the payment via EDI 820 (payment order).
4. Enhanced Financial Reporting and Audit Trail
Now, the same retail store can use EDI technology to automate their financial reporting. By integrating EDI within your accounting system all transactions are processed automatically, and financial data is updated in real-time, allowing for up-to-the-minute reporting and analysis
Conclusion
Now you know why EDI plays such a crucial role in accounting from automating data exchange, reducing errors, and improving efficiency, EDI has become an indispensable tool for modern financial management. The journey towards fully integrated, automated accounting processes may be complex, but the rewards in terms of operational efficiency, cost savings, and strategic advantage make it a journey well worth undertaking.
Commport EDI Solutions for Accounting
Need Help? Download: EDI Buyers Guide
Unlock the full potential of your supply chain with our comprehensive EDI Buyer's Guide — your first step towards seamless, efficient, and error-free transactions
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, EDI transactions use encryption, authentication protocols, and secure communication channels to protect sensitive financial data. Compliance with standards such as GDPR, and ISO 27001 ensures data privacy and security.
EDI integration streamlines accounts payable, receivable, and reconciliation processes by automatically processing transactions, reducing paperwork, and ensuring real-time data accuracy. It allows accounting software to communicate directly with trading partners’ systems, reducing processing time and improving compliance.
EDI maintains accurate and time-stamped records of all transactions, making it easier for businesses to comply with tax regulations and conduct audits. Digital transaction logs enhance financial reporting accuracy and reduce compliance risks.
Almost all industries can benefit from using EDI for streamlining their accounting process. Here are some major ones, retail, healthcare, manufacturing, logistics, and finance benefit from EDI integration in accounting. It enables them to automate financial transactions, reduce processing costs, and improve supply chain efficiency.
Key EDI transactions in accounting include:
- EDI 810 – Invoice
- EDI 820 – Payment Order/Remittance Advice
- EDI 850 – Purchase Order
- EDI 855 – Purchase Order Acknowledgment
- EDI 856 – Advance Ship Notice
- EDI 997 – Functional Acknowledgment