Introduction
Warehouses form the backbone of supply chains, acting as critical hubs for storing, managing, and distributing goods efficiently. In today’s fast-paced logistics environment, ensuring seamless warehouse operations is key to meeting customer demands and maintaining competitiveness. EDI in warehousing is a transformative technology that enables efficient warehouse management. By automating the exchange of business documents, EDI enhances accuracy, speed, and collaboration among supply chain stakeholders.
Let us delve into the history of warehouses, the integration of EDI into warehouse operations, its benefits, and how it powers the efficiency of warehouses and third-party logistics (3PL) providers.
Key Takeaways
- Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) has become a cornerstone of modern warehouse management, automating document exchange and enhancing supply chain efficiency.
- Warehouses have evolved from simple storage spaces in ancient times to high-tech facilities, with EDI marking a significant leap in digital adoption.
3. Operational Benefits:
- Enhanced accuracy in inventory tracking and order processing
- Faster operations for goods receipt, stock allocation, and dispatch
- Cost reduction through elimination of paper-based workflows
- Improved collaboration among supply chain stakeholders
- Real-time visibility into stock levels and shipment statuses
4. Critical EDI Transactions:
- EDI 850 (Purchase Order): Streamlines order receipt
- EDI 856 (Advance Shipping Notice): Facilitates preparation for incoming shipments
- EDI 810 (Invoice): Automates billing processes
- EDI 846 (Inventory Inquiry/Advice): Enables real-time stock level updates
What is a Warehouse?
A warehouse is a facility for storing goods and materials until they are distributed to their final destination.
Warehouses support a wide range of activities, including:
- Inventory Management: Ensuring accurate stock levels.
- Order Fulfillment: Picking, packing, and dispatching orders.
- Logistics Support: Streamlining goods movement within the supply chain.
Public warehouses, private warehouses, bonded warehouses, and distribution centers are types of warehouses, each serving specific industries and operational needs.
History of Warehouse Industry
The concept of warehouses has evolved significantly:
Ancient Era
- Early warehouses were simple storage spaces used by merchants in Mesopotamia and Egypt to store grains and other commodities.
- These served as centralized locations for trade and stock management.
Industrial Revolution
- The 18th and 19th centuries saw the rise of large warehouses near ports and railway hubs to support mass production and distribution.
- Mechanized systems like conveyor belts started appearing during this era.
20th Century
- Warehouses transformed into high-tech facilities as globalization increased demand for more efficient logistics.
- The introduction of forklifts, pallets, and barcode systems revolutionized warehouse operations.
Early Digital Adoption
The 20th century also marked the beginning of digital adoption in warehouses:
- Inventory Control Systems: Early computer systems were implemented to track stock levels.
- Barcode Technology: Introduced in the 1970s, barcodes revolutionized inventory tracking.
- Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): Software systems emerged in the 1990s to automate warehouse operations.
While these technologies improved efficiency, their true potential was unlocked with the advent of EDI, enabling seamless communication between systems.
How to Use EDI in Warehousing Operations
EDI automates exchanging critical documents between trading partners, such as purchase orders and shipping notifications. Here’s how EDI facilitates smooth warehouse operations:
Order Management
- EDI simplifies the order receipt through automated EDI 850 (Purchase Order) transactions.
Inventory Updates
- Real-time stock level updates are exchanged via EDI 846 (Inventory Inquiry/Advice), ensuring accuracy.
Shipping Notifications
- Advance shipment details are communicated using EDI 856 (Advance Shipping Notice), allowing warehouses to prepare for inbound goods.
Invoice Processing
- Automates billing processes with EDI 810 (Invoice), reducing errors and delays.
How Using EDI in Warehousing Enhances 3PL Efficiency
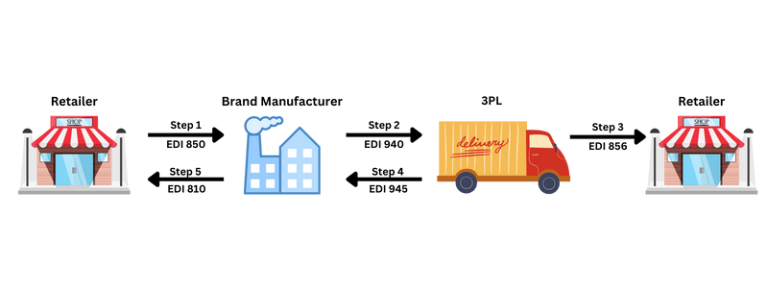
Streamlined Communication
EDI automates information exchange, reducing delays caused by manual processes.
Error Reduction
Automated data entry minimizes human errors, ensuring data accuracy across warehouse operations.
Faster Turnaround Times
By enabling real-time document exchange, EDI accelerates the receiving, processing, and shipping of goods.
Improved 3PL Collaboration
Third-party logistics providers benefit from seamless integration with their clients’ systems, enhancing transparency and efficiency.
Integrating the WMS System into EDI Solutions
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) is a software solution that manages warehouse operations. Integrating WMS with EDI solutions offers:
Real-Time Visibility
- EDI ensures WMS systems are updated in real-time, improving decision-making.
End-to-End Automation
- From order placement to shipping, EDI integrates with WMS for automated workflows.
Enhanced Scalability
- Enables warehouses to handle higher order volumes efficiently without additional manual effort.
Steps to Integrate WMS with EDI
Step 1 – Assess Compatibility
Ensure your WMS supports EDI standards like ANSI X12 or EDIFACT.
Step 2 – Choose an EDI Provider
Opt for a provider with expertise in WMS integration.
Step 3 – Map Data
Align WMS data formats with EDI transaction standards.
Step 4 – Test and Validate
Conduct tests to verify data accuracy and system performance.
EDI in Warehousing Industry - List of Common EDI X12 Transactions Used in the Warehouse Operations
Here are key EDI transactions relevant to warehouses:
EDI 861- Receiving Advice/Acceptance Certificate
EDI 940: Warehouse Shipping Order
EDI 945: Warehouse Shipping Advice
EDI 943: Warehouse Stock Transfer Shipment Advice
EDI 944: Warehouse Stock Transfer Receipt Advice
EDI 947- Warehouse Inventory Adjustment Advice
EDI 997 – Functional Acknowledgement
EDI 846: Inventory Inquiry/Advice
EDI 850: Purchase Order
EDI 856: Advance Shipping Notice
EDI 810: Invoice
EDI 861: Receiving Advice/Acceptance Certificate
Purpose:
EDI 861 is used to communicate the receipt and inspection results of goods. It confirms whether the received goods match the expected quantity and quality as specified in the purchase order.
Details:
- Sender: The receiver of the goods (usually the buyer or warehouse).
- Recipient: The supplier or vendor.
- Use Cases:
- Reporting discrepancies or damages.
- Notifying suppliers of acceptance or rejection of goods.
- Documenting evidence for quality assurance.
Key Data Elements:
- Receipt date and time.
- Details of items received (quantities, serial numbers, or lot numbers).
- Reasons for acceptance or rejection.
EDI 940: Warehouse Shipping Order
Purpose:
EDI 940 provides instructions from a business (typically a retailer or manufacturer) to a third-party warehouse to ship goods to a designated location.
Details:
- Sender: The buyer or retailer.
- Recipient: The warehouse.
- Use Cases:
- Streamlining warehouse shipping processes.
- Automating shipping orders to avoid manual errors.
Key Data Elements:
- Shipping address.
- Item quantities and descriptions.
- Special shipping instructions.
- Delivery deadlines.
EDI 945: Warehouse Shipping Advice
Purpose:
EDI 945 communicates that a shipment has been made from the warehouse, providing details about the shipped items.
Details:
- Sender: The warehouse.
- Recipient: The buyer or retailer.
- Use Cases:
- Confirming shipment details.
- Supporting inventory updates and tracking.
Key Data Elements:
- Shipped quantities.
- Carrier and tracking information.
- Shipment date.
EDI 943: Warehouse Stock Transfer Shipment Advice
Purpose:
EDI 943 informs a warehouse that goods have been shipped from a supplier or another facility.
Details:
- Sender: The supplier or originating warehouse.
- Recipient: The destination warehouse.
- Use Cases:
- Coordinating stock transfers.
- Ensuring accurate receipt of goods at the destination warehouse.
Key Data Elements:
- Shipment details (quantities, SKUs, etc.).
- Origin and destination addresses.
EDI 944: Warehouse Stock Transfer Receipt Advice
Purpose:
EDI 944 confirms the receipt of stock transferred to a warehouse.
Details:
- Sender: The receiving warehouse.
- Recipient: The originating warehouse or supplier.
- Use Cases:
- Verifying the receipt of transferred inventory.
- Documenting discrepancies between shipped and received quantities.
Key Data Elements:
- Received quantities.
- Item details.
- Receipt date and any discrepancies.
. EDI 947: Warehouse Inventory Adjustment Advice
Purpose:
EDI 947 notifies of inventory adjustments due to various reasons, such as damage, miscounts, or shrinkage.
Details:
- Sender: The warehouse.
- Recipient: The buyer or inventory manager.
- Use Cases:
- Keeping inventory records accurate.
- Reporting shrinkage, returns, or spoilage.
Key Data Elements:
- Adjustment reason codes.
- Item details and quantities adjusted.
- Date of adjustment.
EDI 856: Advance Shipping Notice (ASN)
Purpose:
EDI 856 informs the recipient of an upcoming shipment, detailing contents and shipment specifications.
Details:
- Sender: The supplier or shipper.
- Recipient: The buyer or retailer.
- Use Cases:
- Allowing preparation for incoming shipments.
- Streamlining receiving processes.
Key Data Elements:
- Carrier details and tracking number.
- Shipment contents and quantities.
- Estimated delivery date and time.
EDI 846: Inventory Inquiry/Advice
Purpose:
EDI 846 provides inventory status information, including stock availability or quantity updates.
Details:
- Sender: A supplier or warehouse.
- Recipient: The buyer or retailer.
- Use Cases:
- Facilitating inventory management.
- Informing stock replenishment decisions.
Key Data Elements:
- Item details and available quantities.
- Warehouse locations.
EDI 850: Purchase Order
Purpose:
EDI 850 is a standard purchase order sent from a buyer to a supplier to request goods or services.
Details:
- Sender: The buyer.
- Recipient: The supplier.
- Use Cases:
- Automating the order process.
- Providing clear instructions for product delivery.
Key Data Elements:
- Product details (SKUs, descriptions, quantities).
- Delivery address.
- Payment terms.
EDI 810: Invoice
Purpose:
EDI 810 is a digital invoice sent from a supplier to a buyer requesting payment for delivered goods or services.
Details:
- Sender: The supplier.
- Recipient: The buyer.
- Use Cases:
- Facilitating prompt payments.
- Reducing invoice processing errors.
Key Data Elements:
- Invoice number and date.
- Total amount and payment terms.
- Line-item details of purchased goods or services.
Benefits of Using EDI in Warehouse Operations
- Enhanced Accuracy
Minimizes manual data entry errors in inventory tracking and order processing.
- Faster Operations
Speeds up processes like goods receipt, stock allocation, and dispatch.
- Cost Efficiency
Reduces administrative costs associated with paper-based workflows.
- Better Collaboration
Facilitates smooth communication between warehouses, suppliers, and logistics providers.
- Real-Time Updates
Provides instant visibility into stock levels, shipment statuses, and order fulfillment.
Conclusion
The integration of EDI into warehouse operations has revolutionized the logistics landscape. By automating data exchange, EDI enhances accuracy, efficiency, and collaboration, making it a cornerstone of modern warehouse management.
For businesses looking to stay competitive, adopting EDI is not just an option but a necessity. Coupled with advanced WMS solutions, EDI ensures warehouses operate at peak performance, driving success across supply chains.
Commport EDI Solutions
Frequently Asked Questions
EDI streamlines communication between 3PL providers and their clients, improving transparency, accuracy, and efficiency in logistics operations.
WMS manages warehouse operations, while EDI enables automated document exchange between systems for seamless communication.
Yes, cloud-based EDI solutions make it affordable and accessible for small and medium-sized warehouses.
EDI provides real-time stock level updates, ensuring accurate inventory tracking and reducing overstock or stockouts.
Yes, modern EDI solutions use encryption and secure communication protocols to protect sensitive data.