Introduction
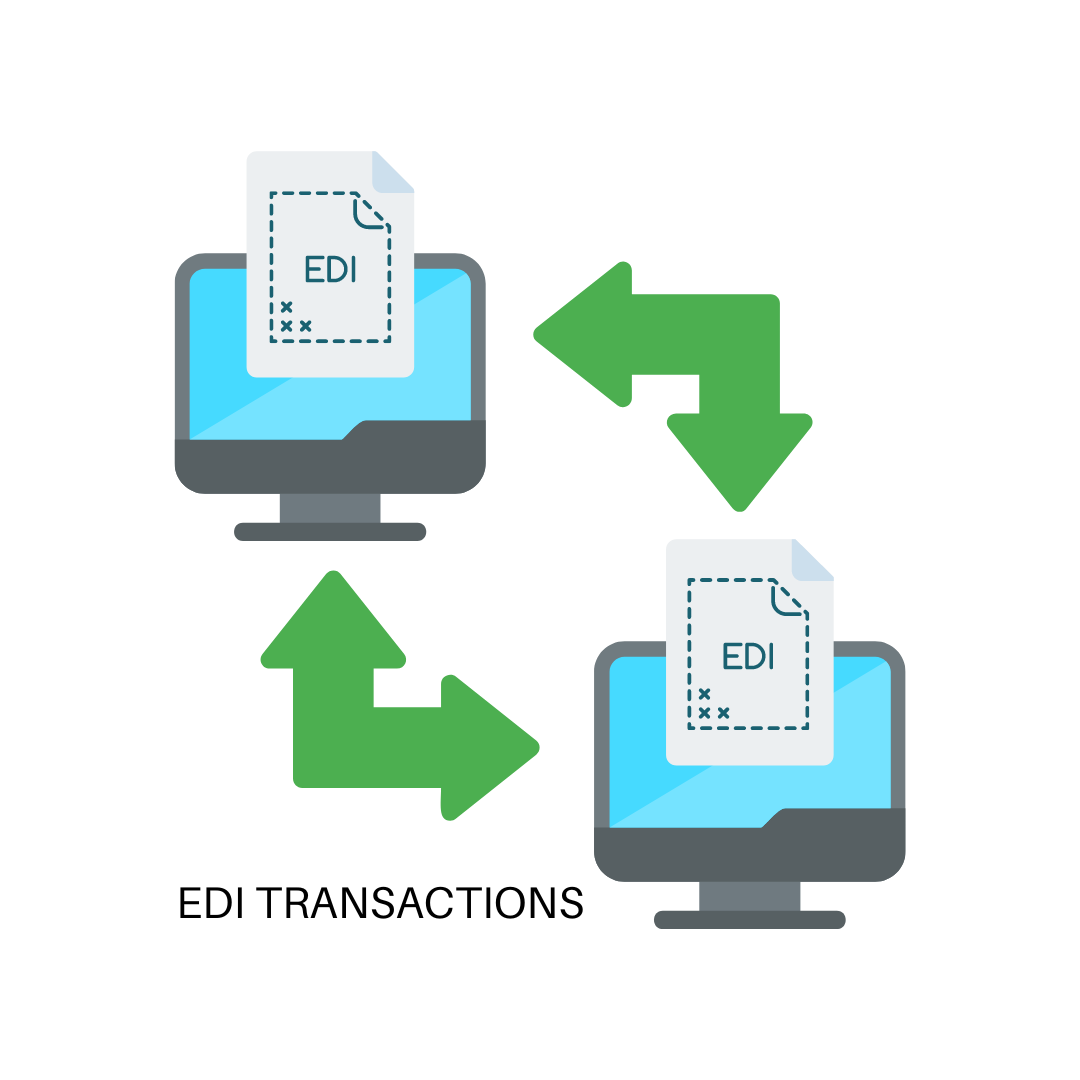
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) has emerged as a powerful technology that enables businesses to exchange documents electronically in a standardized and efficient manner. One of the key advantages of EDI is its ability to increase the speed of document transactions. In this blog post, we will explore what EDI transactions are, how they work, and how EDI can enhance the speed of document transactions.
Key Takeaways
- EDI Transactions are standardized electronic documents used to exchange business data, such as purchase orders and invoices, between trading partners.
- They follow specific formats (e.g., X12, EDIFACT) to ensure compatibility across different systems.
- Common EDI documents include EDI 850 (Purchase Order), EDI 810 (Invoice), and EDI 856 (Advanced Shipping Notice).
- Automating EDI file processing reduces manual errors, speeds up processing, and ensures compliance with partner requirements.
- EDI streamline supply chain operations, enhancing efficiency and accuracy in business communication.
What are EDI Transactions?
EDI transactions refer to the electronic exchange of business documents between trading partners using standardized formats and protocols. These transactions enable businesses to seamlessly share a wide range of documents, including purchase orders, invoices, shipping notices, and more, in a structured and machine-readable format.
EDI transactions are based on established standards such as ANSI X12 and EDIFACT. These standards define the structure and content of various types of business documents, ensuring compatibility and consistent interpretation of data between trading partners.
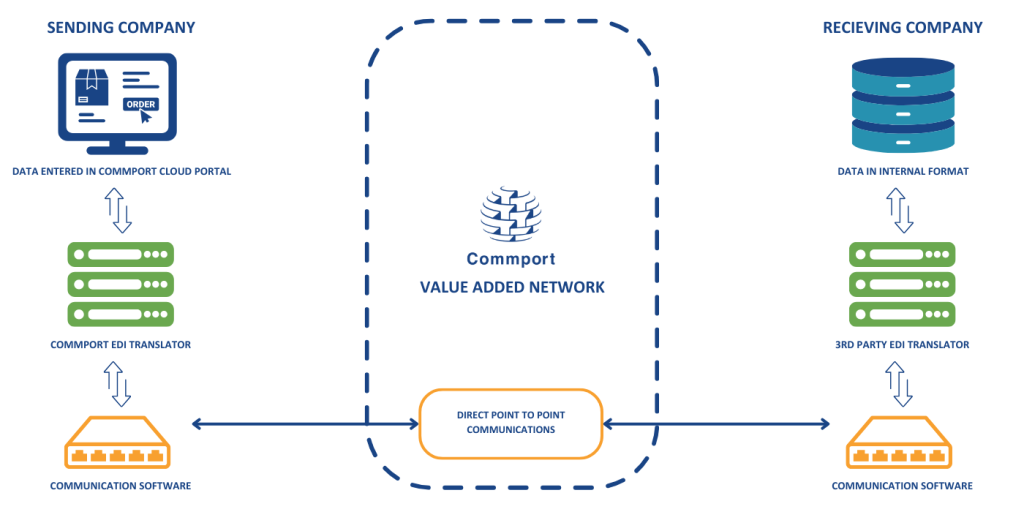
How EDI Transactions Work?
Step by step process,
1. Document Preparation
Each trading partner prepares their respective documents (e.g., purchase orders or invoices) in their internal systems, adhering to the relevant EDI standards. The document data is transformed into the corresponding EDI format, which is typically a structured electronic file.
2. Transmission
The EDI documents are electronically transmitted from the sender’s system to the receiver’s system. This transmission can occur through various methods, such as direct point-to-point connections, Value-Added Networks (VANs), or secure file transfer protocols (e.g., AS2 or sFTP).
3. Document Translation
Upon receiving the EDI documents, the receiver’s system translates the data from the standardized EDI format back into a format compatible with their internal systems. This EDI translation process ensures that the data can be accurately processed and integrated within the recipient’s business processes.
4. Data Integration
Once translated, the received EDI documents are seamlessly integrated into the recipient’s system for further processing. This integration often involves automated data validation, verification against business rules, and integration with relevant applications such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) or accounting systems.
How can EDI Help 10X the Speed of Document Transactions?
EDI offers several key advantages that contribute to increased speed in document transactions:
1. Elimination of Manual Processes
With traditional paper-based transactions, documents must be physically printed, mailed, or faxed, resulting in significant delays. EDI eliminates these manual processes, enabling the electronic transmission of documents in seconds or minutes, regardless of the physical location of the trading partners.
2. Real-time Data Exchange
EDI facilitates real-time data exchange between trading partners. This means that as soon as a document is sent, it can be received, translated, and integrated into the recipient’s systems without manual intervention. Real-time data exchange significantly reduces processing time and accelerates transaction cycles.
3. Automation and Error Reduction
EDI transactions automate data entry and processing, reducing the chances of errors and eliminating the need for manual reconciliation. By removing manual tasks, such as data entry or document verification, businesses can process documents quickly and accurately, leading to faster transaction cycles.
4. Streamlined Workflows
EDI enables the seamless integration of documents into internal systems and processes. This streamlining of workflows eliminates bottlenecks and manual handoffs, resulting in faster document processing, improved efficiency, and reduced cycle times.
5. Enhanced Visibility and Tracking
EDI provides real-time visibility into the status of document exchanges. Trading partners can track the progress of documents, monitor their delivery, and quickly identify any potential issues or delays. This visibility enables proactive management and faster resolution of any transactional issues.
Here are some of the most common types of documents exchanged,
- Purchase orders
- Invoices
- Shipping notices
- Inventory receipts
- Advance shipment notices
- Payment Advice
Conclusion
EDI revolutionize document exchange processes, enabling businesses to increase the speed of transactions and enhance overall operational efficiency. By eliminating manual processes, facilitating real-time data exchange, automating workflows, and providing enhanced visibility, EDI accelerates document processing cycles and reduces transactional delays. Embracing EDI technology empowers businesses to operate at the speed of today’s digital landscape, facilitating faster order fulfillment, improved customer satisfaction, and streamlined business operations.
Ready to find out more about Commport EDI Solutions & Translation Services
Download: EDI Buyers Guide
Unlock the full potential of your supply chain with our comprehensive EDI Buyer's Guide — your first step towards seamless, efficient, and error-free transactions
Frequently Asked Questions
An EDI transaction is the electronic exchange of standardized business documents between trading partners using the Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) format. Unlike traditional paper-based methods or non-standardized electronic communication, EDI transactions follow a universal format for seamless and efficient data exchange
EDI can involve various business document transactions, including purchase orders, invoices, shipping notices, and more. The specific documents exchanged depend on the nature of the business transaction and the requirements of the trading partners involved.
EDI documents adhere to standardized formats, reducing the risk of errors associated with manual data entry. By eliminating the need for rekeying information and using predefined data structures, EDI enhances data accuracy and minimizes discrepancies in business documents.
While EDI documents follow standardized formats to ensure interoperability, businesses can customize certain elements to meet their specific requirements. However, it’s essential to maintain adherence to agreed-upon standards to facilitate seamless communication with trading partners.
Businesses can initiate EDI transactions by using EDI software or working with a Value-Added Network (VAN). A VAN acts as an intermediary that securely facilitates the exchange of EDI transactions between trading partners. It provides a centralized platform for transmitting, receiving, and managing EDI data, enhancing the reliability and security of the entire process.